The Meaning and Importance of Management
Explain the meaning and importance of management
Management
– act of allocating resources to accomplish desired goals and
objectives efficiently and effectively. Management comprises planning, organizing, staffing, leading or directing, and controlling an organization (a group of one or more people or entities) or effort for the purpose of accomplishing a goal.or is the organization and coordination of the activities of a business in order to achieve defined objectives. Or isThe activities associated with running a company, such as controlling, leading, monitoring, organizing, and planning.
objectives efficiently and effectively. Management comprises planning, organizing, staffing, leading or directing, and controlling an organization (a group of one or more people or entities) or effort for the purpose of accomplishing a goal.or is the organization and coordination of the activities of a business in order to achieve defined objectives. Or isThe activities associated with running a company, such as controlling, leading, monitoring, organizing, and planning.
Principles of Management
Management principles are guidelines for the decisions and actions of managers.
- Division of Work
– According to this principle the whole work is divided into small
tasks.The specialization of the workforce according to the skills of a
person , creating specific personal and professional development within
the labour force and therefore increasing productivity; leads to
specialization which increases the efficiency of labour. - Authority and Responsibility
– This is the issue of commands followed by responsibility for their
consequences. Authority means the right of a superior to give enhance
order to his subordinates; responsibility means obligation for
performance. - Discipline – It is obedience,
proper conduct in relation to others, respect of authority, etc. It is
essential for the smooth functioning of all organizations. - Unity of Command
– This principle states that each subordinate should receive orders and
be accountable to one and only one superior. If an employee receives
orders from more than one superior, it is likely to create confusion and
conflict. - Unity of Direction – All related
activities should be put under one group, there should be one plan of
action for them, and they should be under the control of one manager. - Subordination of Individual Interest to Mutual Interest
– The management must put aside personal considerations and put company
objectives firstly. Therefore the interests of goals of the
organization must prevail over the personal interests of individuals. - Remuneration
– Workers must be paid sufficiently as this is a chief motivation of
employees and therefore greatly influences productivity. The quantum and
methods of remuneration payable should be fair, reasonable and
rewarding of effort. - The Degree of Centralization
– The amount of power wielded with the central management depends on
company size. Centralization implies the concentration of decision
making authority at the top management. - Line of Authority/Scalar Chain
– This refers to the chain of superiors ranging from top management to
the lowest rank. The principle suggests that there should be a clear
line of authority from top to bottom linking all managers at all levels. - Order
– Social order ensures the fluid operation of a company through
authoritative procedure. Material order ensures safety and efficiency in
the workplace. Order should be acceptable and under the rules of the
company. - Equity – Employees must be treated
kindly, and justice must be enacted to ensure a just workplace. Managers
should be fair and impartial when dealing with employees, giving equal
attention towards all employees. - Stability of Tenure of Personnel
– Stability of tenure of personnel is a principle stating that in order
for an organization to run smoothly, personnel (especially managerial
personnel) must not frequently enter and exit the organization. - Initiative
– Using the initiative of employees can add strength and new ideas to
an organization. Initiative on the part of employees is a source of
strength for organization because it provides new and better ideas.
Employees are likely to take greater interest in the functioning of the
organization.
Esprit de Corps
– This refers to the need of managers to ensure and develop morale in
the workplace; individually and communally. Team spirit helps develop an
atmosphere of mutual trust and understanding. Team spirit helps to
finish the task on time.
– This refers to the need of managers to ensure and develop morale in
the workplace; individually and communally. Team spirit helps develop an
atmosphere of mutual trust and understanding. Team spirit helps to
finish the task on time.
LEVELS OF MANAGEMENT.
The term “Levels of Management’
refers to a line of demarcation between various managerial positions in
an organization. The number of levels in management increases when the
size of the business and work force increases and vice versa. The level
of management determines a chain of command, the amount of authority
& status enjoyed by any managerial position. The levels of
management can be classified in three broad categories:
refers to a line of demarcation between various managerial positions in
an organization. The number of levels in management increases when the
size of the business and work force increases and vice versa. The level
of management determines a chain of command, the amount of authority
& status enjoyed by any managerial position. The levels of
management can be classified in three broad categories:
- Top level / Administrative level
- Middle level / Executory
- Low level / Supervisory / Operative / First-line managers
Managers at all these levels perform different functions. The role of managers at all the three levels is discussed below:
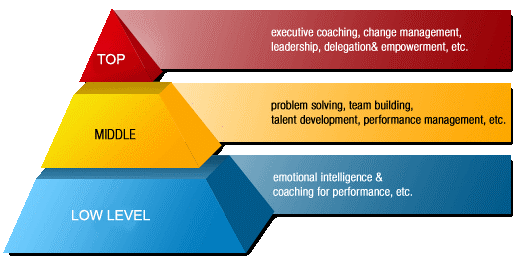
Top Level of Management
It
consists of board of directors, chief executive or managing director.
The top management is the ultimate source of authority and it manages
goals and policies for an enterprise. It devotes more time on planning
and coordinating functions.
consists of board of directors, chief executive or managing director.
The top management is the ultimate source of authority and it manages
goals and policies for an enterprise. It devotes more time on planning
and coordinating functions.
The role of the top management can be summarized as follows –
- Top management lays down the objectives and broad policies of the enterprise.
- It issues necessary instructions for preparation of department budgets, procedures, schedules etc.
- It prepares strategic plans & policies for the enterprise.
- It appoints the executive for middle level i.e. departmental managers.
- It controls & coordinates the activities of all the departments.
- It is also responsible for maintaining a contact with the outside world.
- It provides guidance and direction.
- The top management is also responsible towards the shareholders for the performance of the enterprise.
<!– [if !supportLists]–>1. <!–[endif]–>Middle Level of Management
The
branch managers and departmental managers constitute middle level. They
are responsible to the top management for the functioning of their
department. They devote more time to organizational and directional
functions. In small organization, there is only one layer of middle
level of management but in big enterprises, there may be senior and
junior middle level management. Their role can be emphasized as –
branch managers and departmental managers constitute middle level. They
are responsible to the top management for the functioning of their
department. They devote more time to organizational and directional
functions. In small organization, there is only one layer of middle
level of management but in big enterprises, there may be senior and
junior middle level management. Their role can be emphasized as –
- They execute the plans of the organization in accordance with the policies and directives of the top management.
- They make plans for the subunits of the organization.
- They participate in employment & training of lower level management.
- They interpret and explain policies from top level management to lower level.
- They are responsible for coordinating the activities within the division or department.
- It also sends important reports and other important data to top level management.
- They evaluate performance of junior managers.
- They are also responsible for inspiring lower level managers towards better performance.
Management
Lower
level is also known as supervisory / operative level of management. It
consists of supervisors, foreman, section officers, superintendent etc.
According to R.C. Davis, “Supervisory management refers to
those executives whose work has to be largely with personal oversight
and direction of operative employees”. In other words, they are
concerned with direction and controlling function of management.
level is also known as supervisory / operative level of management. It
consists of supervisors, foreman, section officers, superintendent etc.
According to R.C. Davis, “Supervisory management refers to
those executives whose work has to be largely with personal oversight
and direction of operative employees”. In other words, they are
concerned with direction and controlling function of management.
Their activities include –
- Assigning of jobs and tasks to various workers.
- They guide and instruct workers for day to day activities.
- They are responsible for the quality as well as quantity of production.
- They are also entrusted with the responsibility of maintaining good relation in the organization.
- They communicate workers problems, suggestions, and recommendatory
appeals etc to the higher level and higher level goals and objectives to
the workers. - They help to solve the grievances of the workers.
- They supervise & guide the subordinates.
- They are responsible for providing training to the workers.
- They arrange necessary materials, machines, tools etc for getting the things done.
- They prepare periodical reports about the performance of the workers.
- They ensure discipline in the enterprise.
- They motivate workers.
- They are the image builders of the enterprise because they are in direct contact with the workers.
IMPORTANCE OF MANAGEMENT IN BUSINESS ORGANISATION
- It helps in Achieving Group Goals –
It arranges the factors of production, assembles and organizes the
resources, integrates the resources in effective manner to achieve
goals. It directs group efforts towards achievement of predetermined
goals. By defining objective of organization clearly there would be no
wastage of time, money and effort. Management converts disorganized
resources of men, machines, money etc. into useful enterprise. These
resources are coordinated, directed and controlled in such a manner that
enterprise work towards attainment of goals. - Optimum Utilization of Resources –
Management utilizes all the physical & human resources
productively. This leads to efficacy in management. Management provides
maximum utilization of scarce resources by selecting its best possible
alternate use in industry from out of various uses. It makes use of
experts, professional and these services leads to use of their skills,
knowledge, and proper utilization and avoids wastage. If employees and
machines are producing its maximum there is no under employment of any
resources. - Reduces Costs – It gets maximum
results through minimum input by proper planning and by using minimum
input & getting maximum output. Management uses physical, human and
financial resources in such a manner which results in best combination.
This helps in cost reduction. - Establishes Sound Organization –
No overlapping of efforts (smooth and coordinated functions). To
establish sound organizational structure is one of the objective of
management which is in tune with objective of organization and for
fulfillment of this, it establishes effective authority &
responsibility relationship i.e. who is accountable to whom, who can
give instructions to whom, who are superiors & who are subordinates.
Management fills up various positions with right persons, having right
skills, training and qualification. All jobs should be cleared to
everyone. - Establishes Equilibrium – It enables
the organization to survive in changing environment. It keeps in touch
with the changing environment. With the change is external environment,
the initial co-ordination of organization must be changed. So it adapts
organization to changing demand of market / changing needs of societies.
It is responsible for growth and survival of organization. - Essentials for Prosperity of Society –
Efficient management leads to better economical production which helps
in turn to increase the welfare of people. Good management makes a
difficult task easier by avoiding wastage of scarce resource. It
improves standard of living. It increases the profit which is beneficial
to business and society will get maximum output at minimum cost by
creating employment opportunities which generate income in hands.
Organization comes with new products and researches beneficial for
society.
Disadvantages of management.
- Time consuming in making decision
- high cost of operation i.employees salaries
- conflict among employees
Historical Evolution of Management
Discuss the historical evolution of management
Meaning of Planning; Organization; Staffing; Direction; Control and Coordination
Explain the following functions of management: Planning; Organization; Staffing; Direction; Control and Coordination
FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT
Planning
- The
planning function of management controls all the planning that allows
the organization to run smoothly. Planning involves defining a goal and
determining the most effective course of action needed to reach that
goal. Typically, planning involves flexibility, as the planner must
coordinate with all levels of management and leadership in the
organization. Planning also involves knowledge of the company’s
resources and the future objectives of the business.

Organizing
- The
organizing function of leadership controls the overall structure of the
company. The organizational structure is the foundation of a company;
without this structure, the day-to-day operation of the business becomes
difficult and unsuccessful. Organizing involves designating tasks and
responsibilities to employees with the specific skill sets needed to
complete the tasks. Organizing also involves developing the
organizational structure and chain of command within the company.
Coordinating
- The
coordinating function of leadership controls all the organizing,
planning and staffing activities of the company and ensures all
activities function together for the good of the organization.
Coordinating typically takes place in meetings and other planning
sessions with the department heads of the company to ensure all
departments are on the same page in terms of objectives and goals.
Coordinating involves communication, supervision and direction by
management.
Staffing
- The
staffing function of management controls all recruitment and personnel
needs of the organization. The main purpose of staffing is to hire the
right people for the right jobs to achieve the objectives of the
organization. Staffing involves more than just recruitment; staffing
also encompasses training and development, performance appraisals,
promotions and transfers. Without the staffing function, the business
would fail because the business would not be properly staffed to meet
its goals.
Controlling
- The
controlling function of management is useful for ensuring all other
functions of the organization are in place and are operating
successfully. Controlling involves establishing performance standards
and monitoring the output of employees to ensure each employee’s
performance meets those standards. The controlling process often leads
to the identification of situations and problems that need to be
addressed by creating new performance standards. The level of
performance affects the success of all aspects of the organization.
Principles of Organization
Types of Organisational Structures: their Advantages and Disadvantages!
All
managers must bear that there are two organisations they must deal
with-one formal and the other informal.The formal organisation in
usually delineated by an organisational chart and job descriptions. The
official reporting relationships are clearly known to every
manager.Alongside the formal organisation exists are informal
organisation which is a set of evolving relationships and patterns of
human interaction within an organisation that are not officially
prescribed.
managers must bear that there are two organisations they must deal
with-one formal and the other informal.The formal organisation in
usually delineated by an organisational chart and job descriptions. The
official reporting relationships are clearly known to every
manager.Alongside the formal organisation exists are informal
organisation which is a set of evolving relationships and patterns of
human interaction within an organisation that are not officially
prescribed.
Formal organisational structures are categorised as:
- Line organisational structure.
- Staff or functional authority organisational structure.
- Line and staff organisational structure.
- Committee organisational structure.
- Divisional organisational structure.
- Project organisational structure.
- Matrix organisational structure and
- Hybrid organisational structure.
These organisational structures are briefly described in the following paragraphs:
1. Line Organisational Structure:
A
line organisation has only direct, vertical relationships between
different levels in the firm. There are only line
departments-departments directly involved in accomplishing the primary
goal of the organisation. For example, in a typical firm, line
departments include production and marketing. In a line organisation
authority follows the chain of command.
line organisation has only direct, vertical relationships between
different levels in the firm. There are only line
departments-departments directly involved in accomplishing the primary
goal of the organisation. For example, in a typical firm, line
departments include production and marketing. In a line organisation
authority follows the chain of command.
Exhibit 10.3 illustrates a single line organisational structure.
Features:
- Has only direct vertical relationships between different levels in the firm.
Advantages:
- Tends to simplify and clarify authority, responsibility and accountability relationships
- Promotes fast decision making
- Simple to understand.
Disadvantages:
- Neglects specialists in planning
- Overloads key persons.
Some of the advantages of a pure line organisation are:
- A
line structure tends to simplify and clarify responsibility, authority
and accountability relationships. The levels of responsibility and
authority are likely to be precise and understandable. - A line structure promotes fast decision making and flexibility.
- Because line organisations are usually small, managements and employees have greater closeness.
However, there are some disadvantages also. They are:
- As the firm grows larger, line organisation becomes more ineffective.
- Improved speed and flexibility may not offset the lack of specialized knowledge.
- Managers may have to become experts in too many fields.
- There is a tendency to become overly dependent on the few key people who an perform numerous jobs.
2. Staff or Functional Authority Organisational Structure
The jobs or positions in an organisation can be categorized as:
- Line position: a position in the direct chain of command that is responsible for the achievement of an organisation’s goals and
- Staff position: A position intended to provide expertise, advice and support for the line positions.
The
line officers or managers have the direct authority (known as line
authority) to be exercised by them to achieve the organisational goals.
The staff officers or managers have staff authority (i.e., authority to
advice the line) over the line. This is also known as functional
authority.
line officers or managers have the direct authority (known as line
authority) to be exercised by them to achieve the organisational goals.
The staff officers or managers have staff authority (i.e., authority to
advice the line) over the line. This is also known as functional
authority.
An
organisation where staff departments have authority over line personnel
in narrow areas of specialization is known as functional authority
organisation. Exhibit 10.4 illustrates a staff or functional authority
organisational structure.
organisation where staff departments have authority over line personnel
in narrow areas of specialization is known as functional authority
organisation. Exhibit 10.4 illustrates a staff or functional authority
organisational structure.
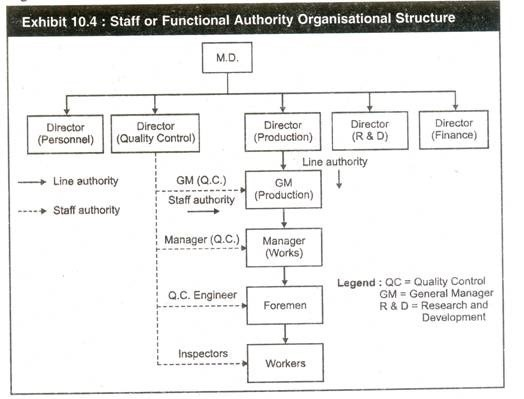
In
the line organisation, the line managers cannot be experts in all the
functions they are required to perform. But in the functional authority
organisation, staff personnel who are specialists in some fields are
given functional authority (The right of staff specialists to issue
orders in their own names in designated areas).
the line organisation, the line managers cannot be experts in all the
functions they are required to perform. But in the functional authority
organisation, staff personnel who are specialists in some fields are
given functional authority (The right of staff specialists to issue
orders in their own names in designated areas).
The
principle of unity of command is violated when functional authority
exists i.e., a worker or a group of workers may have to receive
instructions or orders from the line supervisor as well as the staff
specialist which may result in confusion and the conflicting orders from
multiple sources may lead to increased ineffectiveness. Some staff
specialists may exert direct authority over the line personnel, rather
than exert advice authority (for example, quality control inspector may
direct the worker as well as advise in matters related to quality).
principle of unity of command is violated when functional authority
exists i.e., a worker or a group of workers may have to receive
instructions or orders from the line supervisor as well as the staff
specialist which may result in confusion and the conflicting orders from
multiple sources may lead to increased ineffectiveness. Some staff
specialists may exert direct authority over the line personnel, rather
than exert advice authority (for example, quality control inspector may
direct the worker as well as advise in matters related to quality).
While
this type of organisational structure overcomes the disadvantages of a
pure line organisaional structure, it has some major disadvantages:They
are;
this type of organisational structure overcomes the disadvantages of a
pure line organisaional structure, it has some major disadvantages:They
are;
- the potential conflicts resulting from violation of principle of unity of command and
- the tendency to keep authority centralized at higher levels in the organisation.
3. Line and Staff Organisational Structure:
Most
large organisations belong to this type of organisational structure.
These organisations have direct, vertical relationships between
different levels and also specialists responsible for advising and
assisting line managers. Such organisations have both line and staff
departments. Staff departments provide line people with advice and
assistance in specialized areas (for example, quality control advising
production department).
large organisations belong to this type of organisational structure.
These organisations have direct, vertical relationships between
different levels and also specialists responsible for advising and
assisting line managers. Such organisations have both line and staff
departments. Staff departments provide line people with advice and
assistance in specialized areas (for example, quality control advising
production department).
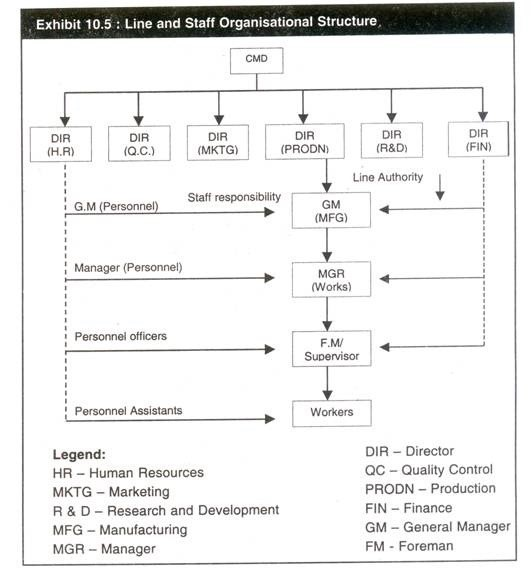
Exhibit
10.5 illustrates the line and staff organisational chart. The line
functions are production and marketing whereas the staff functions
include personnel, quality control, research and development, finance,
accounting etc. The staff authority of functional authority
organisational structure is replaced by staff responsibility so that the
principle of unity of command is not violated.
10.5 illustrates the line and staff organisational chart. The line
functions are production and marketing whereas the staff functions
include personnel, quality control, research and development, finance,
accounting etc. The staff authority of functional authority
organisational structure is replaced by staff responsibility so that the
principle of unity of command is not violated.
Three types of specialized staffs can be identified:
- Advising,
- Service and
- Control.
Some
staffs perform only one of these functions but some may perform two or
all the three functions. The primary advantage is the use of expertise
of staff specialists by the line personnel. The span of control of line
managers can be increased because they are relieved of many functions
which the staff people perform to assist the line.
staffs perform only one of these functions but some may perform two or
all the three functions. The primary advantage is the use of expertise
of staff specialists by the line personnel. The span of control of line
managers can be increased because they are relieved of many functions
which the staff people perform to assist the line.
Some advantages are:
- Even
through a line and staff structure allows higher flexibility and
specialization it may create conflict between line and staff personnel. - Line
managers may not like staff personnel telling them what to do and how
to do it even though they recognize the specialists’ knowledge and
expertise. - Some staff people have difficulty adjusting to the role, especially when line managers are reluctant to accept advice.
- Staff people may resent their lack of authority and this may cause line and staff conflict.
Its Features are:
- Line and staff have direct vertical relationship between different levels.
- Staff specialists are responsible for advising and assisting line managers/officers in specialized areas.
- These types of specialized staff are (a) Advisory, (b) Service, (c) Control e.g.,
- Advisory: Management information system, Operation Research and Quantitative Techniques, Industrial Engineering, Planning etc
- Service: Maintenance, Purchase, Stores, Finance, Marketing.
- Control: Quality control, Cost control, Auditing etc.
The Advantages’
- Use of expertise of staff specialists.
- Span of control can be increased
- Relieves line authorities of routine and specialized decisions.
- No need for all round executives.
The Disadvantages are as follows:
- Conflict between line and staff may still arise.
- Staff officers may resent their lack of authority.
- Co-ordination between line and staff may become difficult.
Committee Organisational Structure Features:
- Formed for managing certain problems/situations
- Are temporary decisions.
Advantages are as follows:
- Committee decisions are better than individual decisions
- Better interaction between committee members leads to better co-ordination of activities
- Committee members can be motivated to participate in group decision making.
- Group discussion may lead to creative thinking.
The Disadvantages are:
- Committees may delay decisions, consume more time and hence more expensive.
- Group action may lead to compromise and indecision.
- ‘Buck passing’ may result.
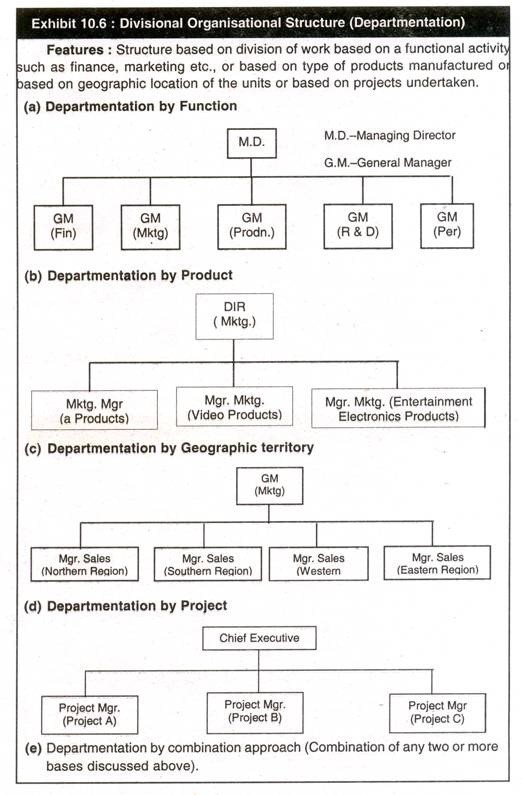
4. Divisional Organisational Structure:
In this type of structure, the organisation can have different basis on which departments are formed. They are:
- Function,
- Product,
- Geographic territory,
- Project and
- Combination approach.
Exhibit 10.6 illustrates organisational structures formed based on the above basis of departmentation.
5. Project Organisational Structure:
The
line, line and staff and functional authority organisational structures
facilitate establishment and distribution of authority for vertical
coordination and control rather than horizontal relationships. In some
projects (complex activity consisting of a number of interdependent and
independent activities) work process may flow horizontally, diagonally,
upwards and downwards. The direction of work flow depends on the
distribution of talents and abilities in the organisation and the need
to apply them to the problem that exists. The cope up with such
situations, project organisations and matrix organisations have emerged.
line, line and staff and functional authority organisational structures
facilitate establishment and distribution of authority for vertical
coordination and control rather than horizontal relationships. In some
projects (complex activity consisting of a number of interdependent and
independent activities) work process may flow horizontally, diagonally,
upwards and downwards. The direction of work flow depends on the
distribution of talents and abilities in the organisation and the need
to apply them to the problem that exists. The cope up with such
situations, project organisations and matrix organisations have emerged.
A
project organisation is a temporary organisation designed to achieve
specific results by using teams of specialists from different functional
areas in the organisation. The project team focuses all its energies,
resources and results on the assigned project. Once the project has been
completed, the team members from various cross functional departments
may go back to their previous positions or may be assigned to a new
project. Some of the examples of projects are: research and development
projects, product development, construction of a new plant, housing
complex, shopping complex, bridge etc.
project organisation is a temporary organisation designed to achieve
specific results by using teams of specialists from different functional
areas in the organisation. The project team focuses all its energies,
resources and results on the assigned project. Once the project has been
completed, the team members from various cross functional departments
may go back to their previous positions or may be assigned to a new
project. Some of the examples of projects are: research and development
projects, product development, construction of a new plant, housing
complex, shopping complex, bridge etc.
Exhibit 10.7 illustrates a project organisational structure.
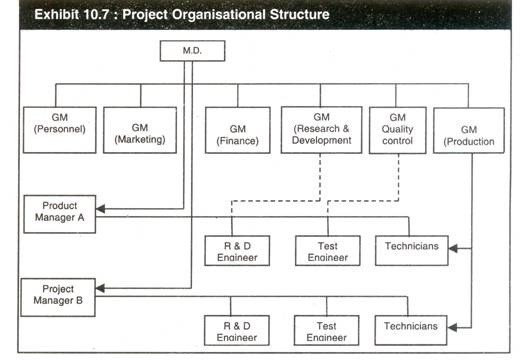
The Features are:
- Temporary
organisation designed to achieve specific results by using teams of
specialists from different functional areas in the organisation.
Importance of Project Organisational Structure:
Project organisational structure is most valuable when:
- Work is defined by a specific goal and target date for completion.
- Work is unique and unfamiliar to the organisation.
- Work is complex having independent activities and specialized skills are necessary for accomplishment.
- Work is critical in terms of possible gains or losses.
- Work is not repetitive in nature.
Characteristics of project organisation:
- Personnel
are assigned to a project from the existing permanent organisation and
are under the direction and control of the project manager. - The
project manager specifies what effort is needed and when work will be
performed whereas the concerned department manager executes the work
using his resources. - The project manager gets the needed support from production, quality control, engineering etc. for completion of the project.
- The
authority over the project team members is shared by project manager
and the respective functional managers in the permanent organisation. - The
services of the specialists (project team members) are temporarily
loaned to the project manager till the completion of the project. - There
may be conflict between the project manager and the departmental
manager on the issue of exercising authority over team members. - Since
authority relationships are overlapping with possibilities of
conflicts, informal relationships between project manager and
departmental managers (functional managers) become more important than
formal prescription of authority. - Full and free communication is essential among those working on the project.
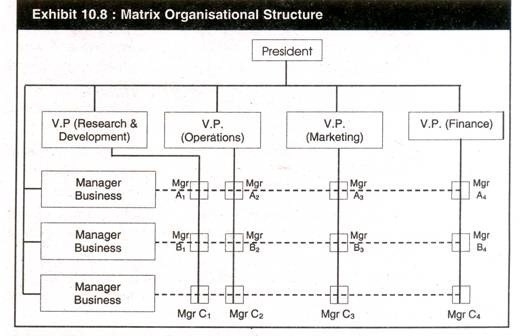
6. Matrix Organisational Structure:
It
is a permanent organisation designed to achieve specific results by
using teams of specialists from different functional areas in the
organisation. The matrix organisation is illustrated in Exhibit 10.8.
is a permanent organisation designed to achieve specific results by
using teams of specialists from different functional areas in the
organisation. The matrix organisation is illustrated in Exhibit 10.8.
Feature:
- Superimposes a horizontal set of divisions and reporting relationships onto a hierarchical functional structure
The Advantages:
- Decentralised decision making.
- Strong product/project co-ordination.
- Improved environmental monitoring.
- Fast response to change.
- Flexible use of resources.
- Efficient use of support systems.
The Disadvantages:
- High administration cost.
- Potential confusion over authority and responsibility.
- High prospects of conflict.
- Overemphasis on group decision making.
- Excessive focus on internal relations.
- This type of organisation is often used when the firm has to be highly responsive to a rapidly changing external environment.
- In
matrix structures, there are functional managers and product (or
project or business group) managers. Functional manager are in charge of
specialized resources such as production, quality control, inventories,
scheduling and marketing. Product or business group managers are
incharge of one or more products and are authorized to prepare product
strategies or business group strategies and call on the various
functional managers for the necessary resources. - The problem
with this structure is the negative effects of dual authority similar to
that of project organisation. The functional managers may lose some of
their authority because product managers are given the budgets to
purchase internal resources. In a matrix organisation, the product or
business group managers and functional managers have somewhat equal
power. There is possibility of conflict and frustration but the
opportunity for prompt and efficient accomplishment is quite high.
7. Hybrid Organisational Structure:
Exhibit 10.9 (a) illustrates the hybrid organisational structure.
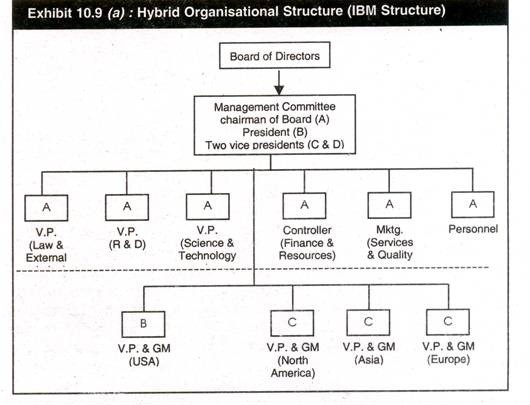
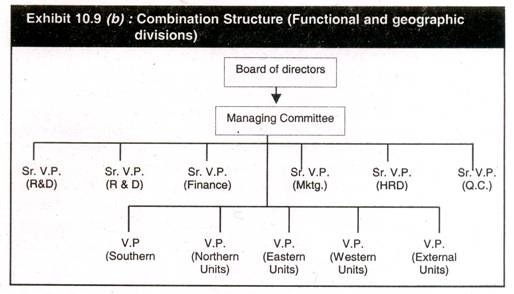
Exhibit 10.9 (b) illustrates a combination structure
Its Advantages:
- Alignment of corporate and divisional goals.
- Functional expertise and efficiency.
- Adaptability and flexibility in divisions.
Its Disadvantages:
- Conflicts between corporate departments and units.
- Excessive administration overhead.
- Slow response to exceptional situations.
Its Uses:
- Used
in organisations that face considerable environmental uncertainty that
can be met through a divisional structure and that also required
functional expertise or efficiency - This type of structure is
used by multinational companies operating in the global environment, for
example, International Business Machines USA. This kind of structure
depends on factors such as degree of international orientation and
commitment. Multinational corporations may have their corporate offices
in the country of origin and their international divisions established
in various countries reporting to the CEO or president at the
headquarters. The international divisions or foreign subsidiaries may be
grouped into regions such as North America, Asia, Europe etc. and again
each region may be subdivided into countries within each region. - While
the focus is on international geographic structures, companies may also
choose functional or process or product departmentation in addition to
geographic pattern while at the head quarter’s the departmentation may
be based on function.
The Informal Organisation:
An
informal organisation is the set of evolving relationships and patterns
of human interaction within an organisation which are not officially
presented. Alongside the formal organisation, an informal organisation
structure exists which consists of informal relationships created not by
officially designated managers but by organisational members at every
level. Since managers cannot avoid these informal relationships, they
must be trained to cope with it
informal organisation is the set of evolving relationships and patterns
of human interaction within an organisation which are not officially
presented. Alongside the formal organisation, an informal organisation
structure exists which consists of informal relationships created not by
officially designated managers but by organisational members at every
level. Since managers cannot avoid these informal relationships, they
must be trained to cope with it
The informal organisation has the following characteristics
- Its members are joined together to satisfy their personal needs (needs for affiliation, friendship etc.)
- It is continuously changing: The informal organisation is dynamic.
- It involves members from various organisational levels.
- It is affected by relationship outside the firm.
- It has a pecking order: certain people are assigned greater importance than others by the informal group.
Even
though an informal organisational structure does not have its own
formal organisational chart, it has its own chain of command:
though an informal organisational structure does not have its own
formal organisational chart, it has its own chain of command:
Benefits of Informal Organisation:
- Assists in accomplishing the work faster.
- Helps to remove weakness in the formal structure.
- Lengthens the effective span of control.
- Compensation for violations of formal organisational principles.
- Provides an additional channel of communication.
- Provides emotional support for employees.
- Encourages better management.
Disadvantages of informal organisation:
- May work against the purpose of formal organisation.
- Reduces the degree of predictability and control.
- Reduces the number of practical alternatives.
- Increases the time required to complete activities.
Principles of organization
- Principle of unity of objectives:
Organizational goals, departmental goals, and individual goals must be
clearly defined. All goals and objectives must have uniformity. When
there is contradiction among different level of goals desired goals
can’t be achieved. Therefore, unity of objectives is necessary - Principle of specialization:
Sound and effective organization believes on organization. The term
specialization is related to work and employees. When an employee takes
special type of knowledge and skill in any area, it is known as
specialization. Modern business organization needs the specialization,
skill and knowledge by this desired sector of economy and thus,
efficiency would be established. - Principle of coordination:
In an organization many equipment, tools are used. Coordination can be
obtained by group effort that emphasize on unity of action. Therefore,
coordination facilitates in several management concepts - Principle of authority:
Authority is the kind of right and power through which it guides and
directs the actions of others so that the organizational goals can be
achieved. It is also related with decision making. It is vested in
particular position, not to the person because authority is given by an
institution and therefore it is legal. It generally flows from higher
level to lowest level of management. There should be unbroken line of
authority. - Principle of responsibility:
Authentic body of an organization is top level management, top level
management direct the subordinates. Departmental managers and other
personnel take the direction from top level management to perform the
task. Authority is necessary to perform the work .only authority is not
provided to the people but obligation is also provided. So the
obligation to perform the duties and task is known as responsibility.
Responsibility can’t be delegated. It can’t be avoided. - Principle of delegation:
Process of transferring authority and creation of responsibility
between superior and subordinates to accomplish a certain task is called
delegation of authority. Authority is only delegated, not
responsibilities in all levels of management. The authority delegated
should be equal to responsibility - Principle of efficiency:
In enterprise different resources are used. Therese resources must be
used in effective manner. When the organization fulfill the objectives
with minimum cost, it is effective. Organization must always concentrate
on efficiency. - Principle of unity of command:
subordinates should receive orders from single superior at a time and
all subordinates should be accountable to that superior. More superior
leads to confusion, delay and so on. - Principle of span of control:
unlimited subordinates cant be supervised by manager, this principle
thus helps to determine numerical limit if subordinates to be supervised
by a manager. This improves efficiency. - Principle of balance:
the functional activities their establishment and other performances
should be balanced properly. Authority, centralization, decentralization
must be balance equally. This is very challenging job but efficient
management must keep it. - Principle of communication:
Communication is the process of transformation of information from one
person to another of different levels. It involves the systematic and
continuous process of telling, listening and understanding opinions
ideas, feelings, information, views etc, in flow of information.
Effective communication is important - Principle of personal ability:
for sound organization, human resources is important. Employees must be
capable. Able employees can perform higher. Mainly training and
development programs must be encouraged to develop the skill in the
employees - Principle of flexibility:
organizational structure must be flexible considering the environmental
dynamism. Sometimes, dramatically change may occur in the organization
and in that condition, organization should be ready to accept the change - Principle of simplicity:
this principles emphasizes the simplicity of organizational structure,
the structure if organization should be simple with minimum number of
levels do that its member an understand duties and authorities.
Sound Policy
Explain the Sound Policy
Line of Authority
Explain the Line of authority
LINE AUTHORITY: The most fundamentalauthoritywithin
an organization, reflects existing superior-subordinate relationships.
It consists of the right to make decisions and to give order concerning
the production,sales or finance related behaviour of subordinates.D
an organization, reflects existing superior-subordinate relationships.
It consists of the right to make decisions and to give order concerning
the production,sales or finance related behaviour of subordinates.D
Simple, Plain and Elaborate Organization
Explain Simple, plain and elaborate organization
Unity – Chain of Command
Explain the Unity – chain of command
Unity
of commandprovides that an employee is responsible to only one
supervisor, who in turn is responsible to only one supervisor, and so on
up the organizational hierarchy. This is true even if the top of the
organization is led by a group of people. For example, imagine you are
the CEO of a technology firm in Silicon Valley. While the board of
directors of your company governs the policy making and strategic
planning, under the concept of unity of command, you do not answer to
all members of the board, but only the chairman of the board.
of commandprovides that an employee is responsible to only one
supervisor, who in turn is responsible to only one supervisor, and so on
up the organizational hierarchy. This is true even if the top of the
organization is led by a group of people. For example, imagine you are
the CEO of a technology firm in Silicon Valley. While the board of
directors of your company governs the policy making and strategic
planning, under the concept of unity of command, you do not answer to
all members of the board, but only the chairman of the board.
Responsibility
Explain the Responsibility
A
duty or obligation to satisfactorily perform or complete a task
(assigned by someone, or created by one’s own promise or circumstances)
that one must fulfill, and which has a consequent penalty for failure.
duty or obligation to satisfactorily perform or complete a task
(assigned by someone, or created by one’s own promise or circumstances)
that one must fulfill, and which has a consequent penalty for failure.
Equity Treatment
Explain the Equity treatment
Measurement of Effectiveness
Explain the Measurement of effectiveness
Measures ofEffectiveness(MOE) Measures ofEffectiveness(MOE) aremeasuredesigned
to correspond to accomplishment of mission objectives and achievement
of desired results. They quantify the results to be obtained by a system
and may be expressed as probabilities that the system will perform as
required.
to correspond to accomplishment of mission objectives and achievement
of desired results. They quantify the results to be obtained by a system
and may be expressed as probabilities that the system will perform as
required.
Span Of Control
Explain the Span of control
Terrance
is a supervisor at MegaCorp, a large, multinational conglomerate. He
works in the product division, overseeing a team that assembles
components for computers. Terrance can only effectively manage a certain
number of people at one time. On the other hand, if he manages too few,
the company will not operate efficiently, and that costs money.
is a supervisor at MegaCorp, a large, multinational conglomerate. He
works in the product division, overseeing a team that assembles
components for computers. Terrance can only effectively manage a certain
number of people at one time. On the other hand, if he manages too few,
the company will not operate efficiently, and that costs money.
The
number of employees that can be controlled directly by a manager is
called the manager’sspan of control. Span of control depends on such
factors as the type of work, the complexity of the work and the
variability of the work task. Let’s look at some examples.
number of employees that can be controlled directly by a manager is
called the manager’sspan of control. Span of control depends on such
factors as the type of work, the complexity of the work and the
variability of the work task. Let’s look at some examples.
Terrance’s
team works in a very controlled environment because of the fragility of
the electronic components, such as motherboards, video cards and audio
cards, that must be installed. Additionally, installation is somewhat
complex and time consuming. Terrance’s span of control is, therefore,
fairly narrow.
team works in a very controlled environment because of the fragility of
the electronic components, such as motherboards, video cards and audio
cards, that must be installed. Additionally, installation is somewhat
complex and time consuming. Terrance’s span of control is, therefore,
fairly narrow.
Let’s
say that Terrance decides to pull some overtime in the packaging
department. Now Terrance is supervising a team that is packing up
Ethernet cables that are sold separately as an accessory. The cables are
pretty durable and all the team is doing is putting individual display
packages into shipping boxes for delivery to the company’s retail
distributors.
say that Terrance decides to pull some overtime in the packaging
department. Now Terrance is supervising a team that is packing up
Ethernet cables that are sold separately as an accessory. The cables are
pretty durable and all the team is doing is putting individual display
packages into shipping boxes for delivery to the company’s retail
distributors.
Given
the relative simplicity of the task, Terrance’s span of control can be
much broader. In other words, he can manage many more employees at the
same time compared to when he is managing his regular team installing
computer components.
the relative simplicity of the task, Terrance’s span of control can be
much broader. In other words, he can manage many more employees at the
same time compared to when he is managing his regular team installing
computer components.
STEPS TAKEN TO SOLVE PROBLEMS HINDERING DEVELOPMENT IN AFRICA AFTER INDEPENDENCE








Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is a very well written article.
I’ll be sure to bookmark it and come back
to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post.
I will certainly return.
Hey there would you mind sharing which blog platform you’re using?
I’m going to start my own blog soon but I’m having a hard time selecting between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and Drupal.
The reason I ask is because your layout seems different then most blogs and I’m looking for something completely unique.
P.S Sorry for getting off-topic but I had to ask!
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is
a very well written article. I will be sure to bookmark it and come back to read
more of your useful info. Thanks for the post. I will
certainly return.
Thanks for sharing, this is a fantastic blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Want more.