TOPIC 3: CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS | BIOLOGY FORM 4
Kingdom Animalia
The word ‘animal’ is derived from the Latin wordanimaliswhich
means ‘having breath’. The Kingdom Animalia is characterized by
eukaryotic and heterotrophic organisms. They are multicellular and lack cell wall. They depend directly or indirectly of plants for their food.
means ‘having breath’. The Kingdom Animalia is characterized by
eukaryotic and heterotrophic organisms. They are multicellular and lack cell wall. They depend directly or indirectly of plants for their food.
Food is ingested and digested in their internal cavity and food reserves are stored as glycogen or fat. Nutrition is holozoic, i.e., by ingestion of food. Animals follow a definite growth pattern, the adults have a definite shape and size. Higher forms of animals exhibitwell developed sensory and neuromotor mechanism.
Most of the organisms are capable of locomotion. Reproduction is by copulation of male and female which is followed bydevelopment in embryonic stages.
General and Distinctive Features of the Kingdom Animalia
Explain general and distinctive features of the kingdom animalia
Distinguishing characteristics of the Kingdom Animalia include:
- Cell type – Eukaryotes
- No cell wall
- Nutrion – Heterotrophic, ingestion
- Body form – Muticellular,(invertebrate/ vertebrate)
- Nervous system – primitive to advanced sensory systems
- Reproduction – All sexual, some also asexual
- Locomotion – Ability to move at some point and time throughlife cycle
General characteristics of the Kingdom Animalia are as follows:
- Animals are eukaryotic, multicellular and heterotrophic organisms.
- They have multiple cells with mitochondria and they depend on other organisms for food.
- Habitat – Most of the animals inhabit seas, fewer are seen in fresh water and even fewer on land.
- There are around 9 to 10 million animal species that inhabit the earth. Only 800,000 species are identified.
- Biologists recognize 36 phyla in the animals kingdom.
- Size
– The sizes of animals ranges from a few celled organism like the
mesozoans to animals weighing many tons like the blue whale. - Animal
bodies – Bodies of animals are made of cells organized into tissues
which perform specific functions. in most animals tissue are organized
into complex organs, which form organ systems. - Cell structure –
The animal cell contains organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria,
Golgi complex, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, vacuoles,
centrioles, cytoskeleton. - Animals are made up of many organ
systems, that aids in performing specific functions that are necessary
for the survival of the organism. - Organ systems are skeletal
system, muscular system, digestive system, respiratory system,
circulatory system, excretory system, reproductive system, immune system
and the endocrine system. - Body symmetry – Most of the animals
are bilaterally symmetrical, while primitive animals are asymmetrical
and cnidarians and echinoderms are radially symmetrical. - Locomotion – Most animals have the ability to move, they show rapid movement when compared to plants and other organisms.
- Respiration
– It is a gaseous exchange of taking in oxygen and giving out carbon
dioxide. This process takes place in organs of respiration like the
lungs, gills, book gills and book lungs and some animals skin is also
used for respiration. - Digestion – Animals ingest food, and
digestion takes place in the internal cavity like the digestive system
in animals, in primitive animals vacuoles are for digestion. - Nervous
system – Sensory mechanism and the coordination of the organ systems is
carried on by the nervous system. In animals the nervous system
comprises of nerve ganglions, or brain, spinal cords and nerves. - Circulatory
system – The distribution of nutrients, exchange of gases and removal
of wastes takes place in the circulatory system. This system comprises
of the heart, blood vessels and the blood. - Excretory system – Removal of wastes from kidneys.
- Skeletal system – support and protection is provided by the skeletal system.
- Reproductive system – Most animals reproduce sexually, by the fusion of haploid cells like the eggs and the sperms.
- Glands of the endocrine system help in control and coordination of the body system.
The major Phyla of the Kingdom Animalia
Mention the major phyta of the kingdom animalia
Kingdom
Animalia has approximately 36 sub-divisions known as ‘phyla’. Each
phyla share particular properties structurally and functionally which
together separate it from other phyla. Below are the most common phyla
classified under traditional biological methodology
Animalia has approximately 36 sub-divisions known as ‘phyla’. Each
phyla share particular properties structurally and functionally which
together separate it from other phyla. Below are the most common phyla
classified under traditional biological methodology
- Phylum Porifera–
They are primitive organisms, most of them are salt-water sponges. They
do not have organs or nerve cells or muscle cells. Approximately, 8,000
species exist today. Example:Sycon, Euspongia, Spongilla.Phylum
Coelentrata (Cnidaria)- This group is composed of jelly-fish and other
lower aquatic animals. Approximately, 15,000 species exist
today.Example:Aurelia, Adamsia. - Phylum Platyhelminthes–
This group consists of flat worms. They inhabit both marine and fresh
water habitats and they are mostly endoparasites found in animals.
Example:Taenia, Fascicola. - Phylum Aschelmeinthes– It is a group of round worms, most of them are parasites. This phylum consists of about 80,000 parasitic worms.
- Phylum Annelida–
They are present in aquatic, terrestrial and are free-living or
parasitic in nature. This phylum comprises of segmented worms. Example:
Earthworm, Leech etc.Phylum Arthropoda- This is the largest phylum which
consists of insects. There are over 1 million species of insects
existing today. Example: Locusts, Butterfly, Scorpion, Prawn. - Phylum Mollusca– It is the second largest phylum. They are terrestrial and aquatic. Example:Pila, Octopus.
- Phylum Echinodermata– This consists of sea stars and sea urchins. There are about 6,000 species. Example:Asteria,Ophiura.
- Phylum Chordata–
Animals of this phylum have a characteristic feature of presence of
notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord and paired pharyngeal gill slits.
Within this phylum advanced group called vertebrates which include fish,
amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals.
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Etymology:-From the Greekplatyfor flat andhelminthesfor worms,Hence Flat Worms
The General and Distinctive Features of the Phylum Platyhelminthes
Explain the general and distinctive features of the phylum platyhelminthes
Characteristics of Platyhelminthes include:
- Bilaterally symmetrical.
- Body having 3 layers of tissues with organs and organelles.
- Body contains no internal cavity.
- Possesses a blind gut (i.e. it has a mouth but no anus)
- Has Protonephridial excretory organs instead of an anus.
- Has normally a nervous system of longitudinal fibres rather than a net.
- Generally dorsoventrally flattened.
- Reproduction mostly sexual as hermaphrodites.
- Mostly they feed on animals and other smaller life forms.
- Some species occur in all major habitats, including many as parasites of other animals.
The Structure of Organism under the Phylum Platyheminthes
Describe the structure of organisms under the phylum latyhelminthes
Platyhelminthes
are mostly worm like creatures that are dorsoventrally flattened,
meaning they look like a ribbon, this is why they are called names such
as Tapeworm, Flatworm, Fluke and Planarian
are mostly worm like creatures that are dorsoventrally flattened,
meaning they look like a ribbon, this is why they are called names such
as Tapeworm, Flatworm, Fluke and Planarian
The
Platyhelminthes are a successful phylum with around 25,000 known
species divided into four classes. Most Platyhelminthes are parasites on
other animals, only the Turbellarians are mostly non-parasitic. A few
species are commensalists living in harmony, or mutual benefit with
another, normally larger organism. Most species feed on animal material
either as parasites or as scavengers, a very few species feed on algae.
Although a few of the free living marine and terrestrial species are
very beautiful, most species are not particularly attractive to the
human mind.
Platyhelminthes are a successful phylum with around 25,000 known
species divided into four classes. Most Platyhelminthes are parasites on
other animals, only the Turbellarians are mostly non-parasitic. A few
species are commensalists living in harmony, or mutual benefit with
another, normally larger organism. Most species feed on animal material
either as parasites or as scavengers, a very few species feed on algae.
Although a few of the free living marine and terrestrial species are
very beautiful, most species are not particularly attractive to the
human mind.
Platyhelminthes
live nearly everywhere, on land, in both fresh and marine waters as
well as inside other animals. Most of the free living species are marine
with only a small number inhabiting fresh water and very few being
terrestrial. Parasitic species normally move between different habitats
as they change life cycle stages and hosts. A number of parasitic
species are of importance to mankind because they infect either our
bodies or the bodies of our livestock. A few species can be fatal to
humans if not treated, but nearly all species can be treated with modern
medicines. Schistosomiasis (Bilharzia) is the most important
platyhelminth disease of humans, causing much suffering and some death,
over 200 million people are infected with the causative agent in
tropical countries.
live nearly everywhere, on land, in both fresh and marine waters as
well as inside other animals. Most of the free living species are marine
with only a small number inhabiting fresh water and very few being
terrestrial. Parasitic species normally move between different habitats
as they change life cycle stages and hosts. A number of parasitic
species are of importance to mankind because they infect either our
bodies or the bodies of our livestock. A few species can be fatal to
humans if not treated, but nearly all species can be treated with modern
medicines. Schistosomiasis (Bilharzia) is the most important
platyhelminth disease of humans, causing much suffering and some death,
over 200 million people are infected with the causative agent in
tropical countries.
While
they remain fairly morphologically simple the Platyhelminthes show
several advance in body structure over the simple radial phyla that came
before them. They have a definite congregation of of sensory organs(a
few have light sensing organs) and nervous tissues at one end of their
body giving them a distinct head and tail. They also have distinct upper
and lower (dorsal and ventral) body surfaces. They have a number of
organs and even the beginnings of organ systems and a more distinct 3rd
layer of cells in their body plan. The evolution of this connective
tissue, called parenchyma, the cells of which serve as storage
reservoirs as well as protecting the internal organs, is a major step
forward toward the more complex body plans of higher animals, such as
humans.
they remain fairly morphologically simple the Platyhelminthes show
several advance in body structure over the simple radial phyla that came
before them. They have a definite congregation of of sensory organs(a
few have light sensing organs) and nervous tissues at one end of their
body giving them a distinct head and tail. They also have distinct upper
and lower (dorsal and ventral) body surfaces. They have a number of
organs and even the beginnings of organ systems and a more distinct 3rd
layer of cells in their body plan. The evolution of this connective
tissue, called parenchyma, the cells of which serve as storage
reservoirs as well as protecting the internal organs, is a major step
forward toward the more complex body plans of higher animals, such as
humans.
However
they still no anus, instead they have only a blind ending gut, or no
gut at all. Those species with a gut must therefore excrete there
digestive waste products through their mouths.
they still no anus, instead they have only a blind ending gut, or no
gut at all. Those species with a gut must therefore excrete there
digestive waste products through their mouths.
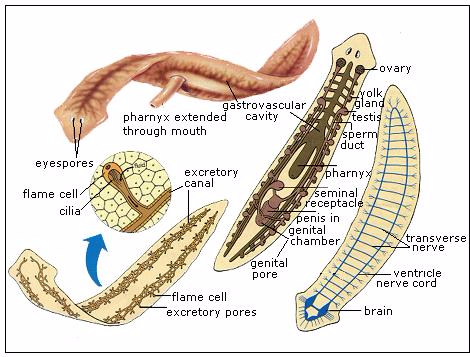
Planarian Anatomy
Phylum Aschelminthes (Nematoda)
General and Distinctive Features of the Phylum Aschelminthes
Explain general and distinctive features of the phylum aschelminthes
Characteristics of Phylum Aschelminthes are:
- Mostly parasitic (in animals and plants), a few free living called as flukes.
- Body is long, cylindrical, fusiform (pointed at both the ends).
- Body wall is composed of cuticle, epidermis and musculature.
- Presence of a false body pseudocoelom not lined by epithelium.
- Digestive system is complete.
- Respiration by simple diffusion.
- Nervous system consists of a nerve ring and many longitudinal nerve cords.
- Only sexual reproduction. Sexes are separate with sexual dimorphism. Males are usually shorter than females
The Structure of Organisms under the Phylum Aschelminthes
Describe the structure of organisms under the phylum aschelminthes
The
Phylum Nematoda (roundworms or nematodes) includes harmless,
soil-dwelling roundworms (nematodes) that eat decaying organic material
or small soil animals. The phylum also includes plant parasites that
infect the roots of plants. These parasitic nematodes decrease the
productivity of many human crops. The phylum includes several human
parasites (see below).
Phylum Nematoda (roundworms or nematodes) includes harmless,
soil-dwelling roundworms (nematodes) that eat decaying organic material
or small soil animals. The phylum also includes plant parasites that
infect the roots of plants. These parasitic nematodes decrease the
productivity of many human crops. The phylum includes several human
parasites (see below).
Like
the Phylum Platyhelminthes, the Phylum Nematoda consists of bilaterally
symmetrical animals that have the organ system level of organization.
the Phylum Platyhelminthes, the Phylum Nematoda consists of bilaterally
symmetrical animals that have the organ system level of organization.
The
Phylum Nematoda differs from the Phylum Platyhelminthes in two
significant ways. First, roundworms have a complete digestive system.
This means that there are two opening to the digestive system. The mouth
at the anterior ingests or swallows food, and the anus at the posterior
releases digestive waste. A complete digestive system is much more
efficient than a cul-de-sac gut. The complete digestive system allows
continuous processing of food. A roundworm can eat continuously, food
digestion can occur continuously, and waste material can be released
continuously. Animals with a cul-de-sac gut must wait until a meal has
been digested, release digestive waste from the mouth, and only then
swallow the next meal.
Phylum Nematoda differs from the Phylum Platyhelminthes in two
significant ways. First, roundworms have a complete digestive system.
This means that there are two opening to the digestive system. The mouth
at the anterior ingests or swallows food, and the anus at the posterior
releases digestive waste. A complete digestive system is much more
efficient than a cul-de-sac gut. The complete digestive system allows
continuous processing of food. A roundworm can eat continuously, food
digestion can occur continuously, and waste material can be released
continuously. Animals with a cul-de-sac gut must wait until a meal has
been digested, release digestive waste from the mouth, and only then
swallow the next meal.
The
second significant difference between the Phylum Nematoda and the
Phylum Platyhelminthes is that the roundworms have a fluid filled body
cavity. The presence of this structure allows space and cushioning for
organs, provides the roundworm with a hydraulic skeleton, and aids in
the distribution of food from the digestive tract to the other cells of
the worm.
second significant difference between the Phylum Nematoda and the
Phylum Platyhelminthes is that the roundworms have a fluid filled body
cavity. The presence of this structure allows space and cushioning for
organs, provides the roundworm with a hydraulic skeleton, and aids in
the distribution of food from the digestive tract to the other cells of
the worm.
Several
human parasites are roundworms. Many people in tropical countries are
infected with hookworm. Immature stages of this parasitic worm burrow
through the skin, travel through the blood vessels to the lungs, enter
the air spaces of the lungs and crawl into the esophagus. The immature
stage is then swallowed. The worm attaches to the intestine with hooks
and matures into an adult. Fertilized eggs are released with feces, and
the zygotes develop into immature stages on soil. When people walk
barefoot over the soil, they become infected. The mature hookworm drinks
blood and lymph juices. They cause anemia due to blood loss.
human parasites are roundworms. Many people in tropical countries are
infected with hookworm. Immature stages of this parasitic worm burrow
through the skin, travel through the blood vessels to the lungs, enter
the air spaces of the lungs and crawl into the esophagus. The immature
stage is then swallowed. The worm attaches to the intestine with hooks
and matures into an adult. Fertilized eggs are released with feces, and
the zygotes develop into immature stages on soil. When people walk
barefoot over the soil, they become infected. The mature hookworm drinks
blood and lymph juices. They cause anemia due to blood loss.
The
human roundworm is common where human feces is used as plant
fertilizer. People ingest eggs when they eat plant material. The
immature stages travel through the human body in blood vessels. Mature
human roundworms live in the intestine where they produced eggs that are
released with feces.
human roundworm is common where human feces is used as plant
fertilizer. People ingest eggs when they eat plant material. The
immature stages travel through the human body in blood vessels. Mature
human roundworms live in the intestine where they produced eggs that are
released with feces.
People
can become accidentally infected with the trichina worm by eating
undercooked port. The muscle of pork may contain immature stages of
trichina worm. When people ingest the larval stage, it matures in the
intestine where the adult worms reproduced. Immature stages migrate from
the intestine to muscle tissue. There the larva forms a cyst. Since
humans aren’t generally eaten, the cysts become coated with calcium
carbonate. This causes muscle stiffness. We call this condition
trichinosis.
can become accidentally infected with the trichina worm by eating
undercooked port. The muscle of pork may contain immature stages of
trichina worm. When people ingest the larval stage, it matures in the
intestine where the adult worms reproduced. Immature stages migrate from
the intestine to muscle tissue. There the larva forms a cyst. Since
humans aren’t generally eaten, the cysts become coated with calcium
carbonate. This causes muscle stiffness. We call this condition
trichinosis.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Roundworms
Outline the advantages and disadvantages of roundworms
Roundworm
parasitesaffect most species of animals and plants, making them
important agricultural pests. There are also several species of
roundworms that live in humans, some nasty, some not. Here are a few…
parasitesaffect most species of animals and plants, making them
important agricultural pests. There are also several species of
roundworms that live in humans, some nasty, some not. Here are a few…
- Trichinella spiralisis
alsoa parasite that has been around for a while, since it has probably
been responsible for several cultures long-standing dietary laws.Trichinellacan
be found around the world, more in temperate zones than the tropics,
mostly in various animals that eat meat, from rats to bears. Humans most
common exposure comes from pork, and pigs commonly pick it up from
eating rats. These worms can live as juveniles in muscle and other
tissues while adults occupy support tissues and the lymphatic system. A
new host becomes infected by eating tissue containing juveniles.
Juveniles become adults and mate in the new hosts intestines, then
females bore out of the intestines, which can cause a wide range of
serious symptoms, settle someplace and begin to release juveniles, which
migrate all over the body, causing damage as they go, until they mostly
coil up in muscle tissues and “wait” for the host to be eaten by a new
host. - Hookwormsinfecta variety of
mammals, with species in cows, dogs, cats, and others, as well as
humans. Hookworms are fairly host-specific – worms of non-human hosts
cant live long in a human. You definitely dont want to catch one of the
hookworms specific to humans, though. They have a very unusual habit for
worms that live in the intestine: instead of living on all of the food
around them, they bite through the intestinal lining and live on blood.
Serious infections occur when bacteria from the intestines get into the
surrounding tissues and/or the blood, and heavy infections can produce
enough blood loss to cause anemia. Its no wonder that one genus is
called - Necator,or “killer”! Hookworm
eggs pass in feces, and juveniles live for a while in the soil if its
nice and wet. The worms get into the next host either by latching on and
boring through their skin, or sticking to paws and getting licked off.
If they come in through the skin, they get into the blood and migrate to
the intestines, usually by way of the lungs, sometimes causing tissue
damage as they go.Hookwormsfor non-human hosts that penetrate human skin
by mistake can wander under the skin, unable to penetrate further, but
the bodys reaction to them can cause a condition sometimes calledcreeping eruption. - Ascarisis
animpressively largeworm, up to 50 centimeters long and about as thick
as a pencil, that lives in human intestines, with maybe as much as a
quarter of the worlds population infected. They aretaken inas
accidentally-swallowed eggs, hatch in the intestine, and the juveniles
bore out, get into the blood, wander the body (where they can cause
problems), emerge in the lungs, grow there for a while (and possibly
cause problems), then migrate up to be swallowed and get back to the
intestines again, where they mate. Females find males by touch (its dark
in an intestine) and crawl into the males hooked tail for mating;
sometimes they mistake the opening of the ducts from the liver or
pancreas for a males tail and get caught, blocking the flow of digestive
juices. A heavy infection can produce aknot of wormsthat blocks
movement of materials through the intestine. Females that cant find
males have been known to migrate up or down the canal, reaching
thenoseor anus in some cases – quite a surprise for the host! Females
lay eggs that pass in feces. The eggs can remain infective in the
environment for years, long after that fecal material has been broken
down. Dirty hands in the mouth explains why children are the most common
hosts for these worms. - Filarial wormsare
a group of roundworms that commonly use biting insects to get juveniles
from host to host, then the adults live in the fluid systems – blood or
lymph systems – of the final host. There are several filarial worms
that infect humans, includingWuchereria,which can block fluid drainage through the lymph system, causing grossswellingof tissues and a form ofelephantiasis. - Onchocercacausesa disease calledriver blindnesswhen
juvenile worms enter and graduallydamagethe eyes (the “river” part is
due to the biting fly carriers being tied to rivers for breeding,
restricting thegeographical rangeof the disease). - Heartwormsarefilarial
parasites of dogs and cats. The juvenile worms are carried by
mosquitos, and the adults settle in the chambers and major vessels of
the heart. Heartworms do not generally infect humans. - Dracunculus medinensis,alsocalled
guinea worms, have been known and written about for centuries (although
often called “serpents” in modern translations), including passages
from Ancient Greek scholars and from the Bible. Adult worms can be as
long as a meter, although they are very thin. As adults, they live in
the tissues under the skin, usually somewhere at and below the hips,
where they may be visible as a white line. After mating, a female
produces huge numbers of eggs that hatch inside her and begin to migrate
out into the surrounding tissue, often causing an allergic reaction
with inflammation and ulceration of the skin (some ancient texts call
them the “fiery serpents” from their effects on the skin). When the skin
breaks, many many tiny juvenile worms may emerge. An opening remains in
the skin through which the female will continue to release young. To
continue theirlife cycle, the juvenile worms must get into open water
and infect a tiny crustacean; for this reason, worms are most active
when the skin is wet.Ancienttreatments, still used in some places,
involve cutting a thin slot in a stick, wetting the skin so the worm
sticks out, catching the writhing worm in the sticks slot, then winding
it slowly out from under the skin. The medical symbol, thecaduceus,of
asnakeorsnakeswrapped around a pole,most likelyis taken from one of the
few effective devices ancient doctors had, a worm-removal stick (worm,
snake; remember, in ancient classification schemes not much distinction
was made among long wriggly things). Worms infect the next host
whenwater containing infected crustaceans is drunk; the juveniles leave
their carriers in the intestine, bore out of the intestine and migrate
to their position under the skin. Humans are affected both by their
allergic reactions to the released juveniles, infections from bacteria
that enter through the broken skin, and worms that stall in deeper
tissues, where they may cause serious damage. Because there is a fairly
simple preventative measure – physically filtering drinking water -this
parasite is very close to being eliminated.
Phylum Annelida
General and Distinctive Features of the Phylum Annelida
Explain general and distrinctive features of the phylum annelida
Characteristics of Annelida:
- Bilaterally symmetrical and vermiform.
- Body has more than two cell layers, tissues and organs.
- Body cavity is a true coelom, often divided by internal septa.
- Body possesses a through gut with mouth and anus.
- Body possesses 3 separate sections, a prosomium, a trunk and a pygidium.
- Has a nervous system with an anterior nerve ring, ganglia and a ventral nerve chord.
- Has a true closed circulatory system.
- Has no true respiratory organs.
- Reproduction normally sexual and gonochoristic or hermaphoditic.
- Feed a wide range of material.
- Live in most environments.
Structure of Organism under the Phylum Annelida (Earthworm)
Describe structure of organism under the phylum annelida (Earthworm)
The
Annelida are a medium sized phylum of more than 9,000 species of worms.
Most species prefer aquatic environments, but there are also a number
of well know terrestrial species. Only a few species of annelids are
commonly known to human beings, these include the delightful Rain, Dew
or Earthworms that work so hard to make our soils healthy, the Ragworms
and Lugworms used by marine fishermen and the much smaller Tubifex or
Red worms used by aquarists to feed their fish. In many countries people
are still familiar with Medicinal leeches, and people who live closer
to nature are naturally more familiar with a much wider range of
Annelids than those who live in cities.
Annelida are a medium sized phylum of more than 9,000 species of worms.
Most species prefer aquatic environments, but there are also a number
of well know terrestrial species. Only a few species of annelids are
commonly known to human beings, these include the delightful Rain, Dew
or Earthworms that work so hard to make our soils healthy, the Ragworms
and Lugworms used by marine fishermen and the much smaller Tubifex or
Red worms used by aquarists to feed their fish. In many countries people
are still familiar with Medicinal leeches, and people who live closer
to nature are naturally more familiar with a much wider range of
Annelids than those who live in cities.
Annelids range in size from the Giant Earthworms, of whichMichrochaetus rappi(Michrochaetus michrochaetus)
is the largest, this magnificent animal has an average length of 1.36 m
(54 ins) and a record breaking specimen has been recorded that measured
6.7 metres (22 ft) in length, it was 2cm (0.8 ins) in diametre. Larger
worms have been reported but not scientifically proven. The smallest
Annelid known to science isChaetogaster annandalaiwhich is full grown at 0.5 mm (0.02 ins).
is the largest, this magnificent animal has an average length of 1.36 m
(54 ins) and a record breaking specimen has been recorded that measured
6.7 metres (22 ft) in length, it was 2cm (0.8 ins) in diametre. Larger
worms have been reported but not scientifically proven. The smallest
Annelid known to science isChaetogaster annandalaiwhich is full grown at 0.5 mm (0.02 ins).
Annelids
have two main modes of existence, they either live rather quietly in
holes or they live more active lives. The basic Annelid body plan is one
of a head followed by a long thin body of numerous similar segments
ending in a small tail. The head consists of a mouth (prostomium) and
sometimes a peristomium, and the tail is more correctly called a
pygidium, as it is not really a tail. Annelids are coelomate animals
meaning they have a true coelom within their body. They have sets
chaetae attached to each body segment, and these can be simple and small
as in the Earthworms or complex and varied as in many Polychaetes. The
head is often reduced and difficult to distinguish in the hole living
species, but may be easily recognised, with eyes and other sensory
devices in those species living a more active life.
have two main modes of existence, they either live rather quietly in
holes or they live more active lives. The basic Annelid body plan is one
of a head followed by a long thin body of numerous similar segments
ending in a small tail. The head consists of a mouth (prostomium) and
sometimes a peristomium, and the tail is more correctly called a
pygidium, as it is not really a tail. Annelids are coelomate animals
meaning they have a true coelom within their body. They have sets
chaetae attached to each body segment, and these can be simple and small
as in the Earthworms or complex and varied as in many Polychaetes. The
head is often reduced and difficult to distinguish in the hole living
species, but may be easily recognised, with eyes and other sensory
devices in those species living a more active life.
Annelids
are coelomate animals (meaning they have a truecoelom, even if this is
reduced secondarily). They normally have long thin bodies composed of a
series of identical segments. These segments lie between the head,
comprised of a prostomium, a mouth and sometimes a peristomium, and a
tail called a pygidium. Growth occurs both laterally, by enlargement of
the segments during the juvenile stages, and through the addition of new
segments. New segments are produced by the foremost section of the
pygidium. In some species they are produced throughout the animals life
but in many species production stops once a certain set number of
segments has been achieved.
are coelomate animals (meaning they have a truecoelom, even if this is
reduced secondarily). They normally have long thin bodies composed of a
series of identical segments. These segments lie between the head,
comprised of a prostomium, a mouth and sometimes a peristomium, and a
tail called a pygidium. Growth occurs both laterally, by enlargement of
the segments during the juvenile stages, and through the addition of new
segments. New segments are produced by the foremost section of the
pygidium. In some species they are produced throughout the animals life
but in many species production stops once a certain set number of
segments has been achieved.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Lumbricus (Earthworm)
Explain advantages and disadvantages of lumbricus (Earthworm)
Despite
the amazing and delicate beauty of polychaetes such as the Fan Worms,
and the huge (really beyond estimation) economic debt owed by mankind to
the Oligochaete Earthworms for their work in soil creation and
maintenance many people still fail to appreciate their true wonder and
beauty.
the amazing and delicate beauty of polychaetes such as the Fan Worms,
and the huge (really beyond estimation) economic debt owed by mankind to
the Oligochaete Earthworms for their work in soil creation and
maintenance many people still fail to appreciate their true wonder and
beauty.
The
earthworms, of which there are many species, are exceedingly important
in soil creation, particularly in temperate areas. Without them,
agriculture and perhaps the whole of human society as we know it would
never have evolved. Like so much of the unnoticed invertebrate world
earthworms are essential to our very existence. In marine environments
the numerous species of Polychaetes play a fundamentally important role
in the maintenance of food chains and the whole ecological balance of
the seas, thus supporting the seemingly endless stocks of fish we like
to eat.
earthworms, of which there are many species, are exceedingly important
in soil creation, particularly in temperate areas. Without them,
agriculture and perhaps the whole of human society as we know it would
never have evolved. Like so much of the unnoticed invertebrate world
earthworms are essential to our very existence. In marine environments
the numerous species of Polychaetes play a fundamentally important role
in the maintenance of food chains and the whole ecological balance of
the seas, thus supporting the seemingly endless stocks of fish we like
to eat.
One
of the strangest ways that humans relate to Annelids is in the hobby of
‘Worm Charming’. This involves enticing earthworms from their holes
(catching them), originally it was a means of acquiring worms for bait,
but now-a-days it is a sport. The world record as far as I know is held
by Tom Shufflebotham who charmed 511 worms from their underground
hideouts from an area of 3 square metres in only 30 minutes during the
1980 Annual Worm Charming Championships held in Cheshire UK. The rules
specify that the worms must be brought to the surface without using
refreshment, stimulation, drugs or digging. Tom used a method called
twanging which involves sticking a 4-pronged pitchfork into the ground
and twanging it.
of the strangest ways that humans relate to Annelids is in the hobby of
‘Worm Charming’. This involves enticing earthworms from their holes
(catching them), originally it was a means of acquiring worms for bait,
but now-a-days it is a sport. The world record as far as I know is held
by Tom Shufflebotham who charmed 511 worms from their underground
hideouts from an area of 3 square metres in only 30 minutes during the
1980 Annual Worm Charming Championships held in Cheshire UK. The rules
specify that the worms must be brought to the surface without using
refreshment, stimulation, drugs or digging. Tom used a method called
twanging which involves sticking a 4-pronged pitchfork into the ground
and twanging it.
Phylum Arthropoda
General and Distinctive Features of the Phylum Arthropoda
Explain general and distinctive features of the phylum arthropoda
Phylum
Anthropoda has more species than any other phylum. An arthropod’s body
plan is segmented just as annelids. They have appendages, which serve a
variety of purposes such as gaseous exchange, food gathering, locomotion
and direction of stimuli.Arthropods have an exoskeleton or cubicle that
is secreted by the epidermis. Their skeleton is made up of chitin.
Anthropoda has more species than any other phylum. An arthropod’s body
plan is segmented just as annelids. They have appendages, which serve a
variety of purposes such as gaseous exchange, food gathering, locomotion
and direction of stimuli.Arthropods have an exoskeleton or cubicle that
is secreted by the epidermis. Their skeleton is made up of chitin.
Their exoskeleton serves different purposes such as:
- Support
- Attachment for muscles; and
- Protection from physical damage
They have jointed appendages used for various functions such as feeding, locomotion and sensory purposes.
Arthropoda
have developed distinct regions of the body, namely the head, thorax
and abdomen. The head possesses sensory receptors such as eyes and
antennae as well as feeding appendages. The head is more developed in
annelids with a larger brain. Some classes of the phylum e.g. insects
have developed flight which greatly increases opportunities for finding
food and escaping from predators.
have developed distinct regions of the body, namely the head, thorax
and abdomen. The head possesses sensory receptors such as eyes and
antennae as well as feeding appendages. The head is more developed in
annelids with a larger brain. Some classes of the phylum e.g. insects
have developed flight which greatly increases opportunities for finding
food and escaping from predators.
Distinctive Features of the Phylum Arthropoda
- They have an exoskeleton made up of a chitin and sometimes-calcareous matter, which may either, be rigid, stiff or flexible.
- Each segment in arthropoda typically bears a pair of jointed appendages used for locomotion or feeding or sensory purposes.
Classes of the Phylum Arthropoda
Mention classes of the phylum arthropoda
Classes of the Phylum Arthropoda include:
- Class: Crustacean
- Class: Insecta
- Class: Chilopoda
- Class: Diplopoda
- Class: Arachnida
Examples of Organisms under each Class of the Phylum Artropoda
Cite examples of organisms under each class of the phylum artropoda
Examples of Organisms under each Class of the Phylum Artropoda include:
- Class Crustacean:Crustacea
is a class of organisms whose bodies are covered by a hard shell called
carapace.Examples of crustaceans are woodlice, water flea, Cray fish,
crabs, lobsters, shrimps and barnacles. - Class Insecta:Insects
are the most successful organisms on earth since they possess an
exoskeleton, which reduces water loss from the body. Insects are the
largest group of arthropods. They occupy every habitat an earth in such
places as air, soil and water. However they mainly inhabit terrestrial
habitats. Examples of insects include grasshoppers, houseflies,
butterflies, bees and termites. - Class Chilopoda: Class Chilopoda is made up of centipedes. The centipede is mainly found on land
- Class Diplopoda:Class Diplopoda is made up of millipedes. Millipedes are common in damp places.
- Class Arachnida:Arachnida are terrestrial arthropods. Examples of arachnids are spiders, ticks, scorpions and mites.
Distinctive Features of each Class of the Phylum Arthropoda
Explain distinctive features of each class of the phylum arthropoda
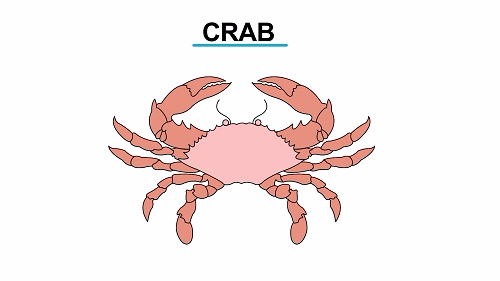
Distinctive features of ClassCrutacean
- Crustacea are mainly found in marine and fresh water thus they occupy aquatic habitats
- Their gaseous exchange is by means of gills or through the body membrane
- Their
bodies are divided into two main parts: the head and thorax are fused
to form a Cephalothorax the second part is the abdomen - They have a pair of compound eyes each on a raised stalk
- They have two antennae
- They have four pairs of mouthparts namely maxilla, mandible, labium and labrum
- They have five pairs of limbs that are modified for swimming
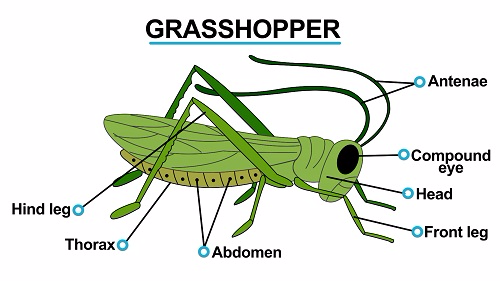
Distinctive features of Class Insecta
- Insets have three body parts namely the head, thorax and abdomen
- They have one pair of antennae
- They have a pair of compound eyes. In some cases simple eyes are also present
- They have three pairs of walking legs per segment of the thorax
- Most insects have one or two pairs of wings on the second or third segment o the thorax. Some insects have no wings
- They breath by means of air holes called spiracles and carry out gaseous exchange through the tracheoles of the tracheal system
- They undergo complete or incomplete metamorphosis with a larva stage
- They mainly occupy terrestrial habitats
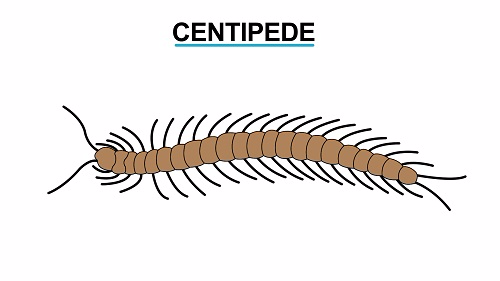
Distinctive features of Class Chilopoda
- Centipedes have a clearly defined head while the rest of the segments are similar
- They have a pair of antennae
- They have one pair of mouthparts known as mandibles
- They have simple and compound eyes, although some lack compound eyes
- They have a pair of legs in each body segment
- They carry out gaseous exchange by means of tracheoles of the tracheal system
- They feed on insects and worms
- They occupy terrestrial habitats
- They have one pair of poison claws
Distinctive features of Class Diplopoda
- Millipedes have a clearly defined head. All the other body segments are basically similar
- They have one pair of antennae
- They have one pair of mouthparts namely, the mandibles
- They have simple and compound eyes, although some lack compound eyes
- They have two pairs of legs in each body segment
- They carry out gaseous exchange through tracheoles of the trachea system
- They feed on plants
- They inhabit terrestrial habitats
- They have a cylindrical body
Distinctive features of Class Arachnida
- Arachnids
have two body parts. The head and thorax are fused to form
cephalothorax or prosoma, the abdomen is referred to as opithosoma. - They do not have mouthparts. However they have one pair of appendages for sensing prey and another pair for capturing the prey
- This pair of appendages is known as chelicerae. Thus they have a carnivorous mode of feeding
- They have simple eyes
- They have four pairs of walking legs
- They carry out gaseous exchange by the lung book or trachea
- A lung book consists of folds of ectoderm with slit like opening on the surface of the abdomen
- Arachnids do not have wings
- They inhabit terrestrial habitats
Structures of Representative Organisms under each Class of Phylum Arthropoda
Describe structures of representative organisms under each class
Structures of Representative Organisms


The Advantages and Disadvantages of the Organisms under each Class of Phylum Arthropoda
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of the organisms under each class of phylum arthropoda
IMPORTANCE OF CRUSTACEANS
- Human beings use crustaceans as food especially lobsters, shrimps, crabs and crayfish
- Some of them are used for decorations in the homes especially crabs and crayfish
- Most crustaceans attract tourists during their visits especially along the beaches
IMPORTANCE OF THE CLASS DIPLOPODA
- The millipedes can be useful like earthworms; they help to aerate the soil
IMPORTANCE OF INSECTS
- Most insects are naturally useful in pollination e.g. bees and flies
- Other
insects e.g. bees are able to make various substances like honey and
wax that are consumed by humans and wax is used for making candles - Some insects like termites and earthworms help to turn the soil over and so keep it lose and aerated
- Most
insects are vectors of several species of disease causing organisms
e.g. mosquito is the vector for plasmodium that causes malaria in
humans. Flies are vectors for filarial worms that cause river blindness
in humans
DISADVANTAGES OF INSECTS
- Many
insects transmit diseases to people by transmitting contaminated
material by means of their appendages e.g. houseflies transmit cholera
by carrying contaminated stool to whatever can be consumed by human
beings.
IMPORTANCE OF ARTHROPODA
- They cause damage to crops and forestry, locusts and some larvae e.g. feed on crops
- They
spread diseases to humans and other domestic animals e.g. female
anopheles spreads malaria, while tsetse flies spread sleeping sickness - They are source of food e.g. green grasshoppers, termites, crabs and shrimps
- They cause damage to household materials e.g. cockroaches damage furniture
- Some members aid pollination e.g. bees, butterflies and lady birds
Phylum Chordata
Phylum chordata is found in the kingom Animalia. Members found on phylum chordata are fish, frog, lizard, birds, rats etc.
General and Distinctive Characteristics Features of the Phylum Chordata
Explain general and distinctive characteristics features of the phylum chordata
General Distinctive Characteristics of Phylum Chordata are:
- They
have a notochord in the embryonic stage. If they notochord persists
throughout the life span, it may be surrounded by a vertebral column as
in lungfish or it may both be surrounded by a vertebral column as in
some chordata - Their nerve cord is hollow and placed dorsally to the gut
- They have gill slits at least during the embryonic stage
- They have tail which is behind the anus
Classes of the Phylum Chordate
Mention classes of the phylum chordate
The phylum chordata consists of six classes which are
- Class Chondrichthyes
- Class Osteichthyes
- Class Amphibia
- Class Reptilia
- Class Aves and
- Class Mammalia
Distinctive Features of Each Class of the Phylum Chordata
Explain distinctive features of each class of the phylum chordata
Distinctive features of Class Chondrichthyes
- The skeleton is made up of cartilage
- The body is covered with placoid scales
- The caudal fin has tow lobes that differ in size
- Each pair of gills is in a separate compartment
- The mouth and two nostrils are ventrally placed
- Males have Copulatory structures called claspers
Distinctive Features of Class Osteichthyes
- The skeleton is made up of bones
- The body is covered with ganoid scales
- The mouth is terminally placed and nostrils are forced on the dorsal surface
- All pairs of gills are found in common chamber and the chambers are covered by an operculum
- The caudal fin has loves of the same size
Distinctive Features of Class Amphibia
- Their skin is always moist example frogs
- Their life cycle involves larva form called tadpole
- They have gills which are present in the early stages of the development of the tadpole
- They have a heart which has three chambers
- There is gaseous exchange by gills in the tadpole and in the adult it takes place in the lungs, skin and the mouth lining
Distinctive features of Birds
- The body is covered with feathers
- The anterior pair of limbs is modified into wings
- The mouth is modified into a beak or bill
Distinctive features of Class Mammalia
- Their body is covered with hairs
- They have mammary glands
- They have teeth of different types and shapes
- They have diaphragm
- Their red blood cells have no nucleus
- They have sweat glands. The body temperature of mammals is constant
Structure of Representative Organisms in each Class of Phylum Chordata
Describe structure of representative organisms in each class of phylum chordata
Structure of Amphibians
The
body of toad or frog consists of a head and trunk only. The skin is dry
and warty in toads and smooth and shiny in frogs. On the head are pair
of nostrils and lower eyelids, which are almost immovable.
body of toad or frog consists of a head and trunk only. The skin is dry
and warty in toads and smooth and shiny in frogs. On the head are pair
of nostrils and lower eyelids, which are almost immovable.
The
fore limbs of toads and frogs are short. They have 4 digits on each
hand, as the thumb is missing. The hind limbs are much longer than the
front ones and the feet are very large. A thin web of skin, which is
particularly well developed in frogs, joins the toes. Adult toads are
mainly land animals and usually enter water only to breed.
fore limbs of toads and frogs are short. They have 4 digits on each
hand, as the thumb is missing. The hind limbs are much longer than the
front ones and the feet are very large. A thin web of skin, which is
particularly well developed in frogs, joins the toes. Adult toads are
mainly land animals and usually enter water only to breed.

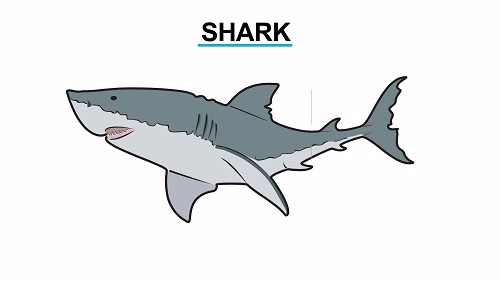
Example of Specimen found on Class Chondrichthyes

Example of Specimen found on Class Chondrichthyes

Example of Specimen found on Class Aves
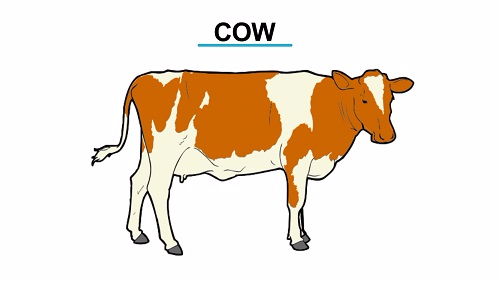
Example of Specimen found on Class Mammalia

Example of Specimen found on Class Reptilia
The advantages and disadvantages of Organisms under each Class of Phylum Chordata
Outline the advantages and disadvantages of organisms under each class of phylum chordata
Importance of Amphibians
- They are ecologically important
- They are used in research specimen
- Some amphibians are eaten as food
- Some amphibians have unique features. Example abnormally big sizes attract tourists
- They have typical characteristics of larger animals hence they are among the most preferred specimens for biological studies
Importance of Class Reptilia
- Reptiles act as attractive features e.g. colour of snake
- Reptiles are used as a source of food for other species example birds feed on snakes
- Reptiles are used in decorations in houses
Disadvantages of Class Reptilia
- Can cause death to human beings, for example a snake
Importance of Birds
- Flesh of several species is used as food for human beings example chicken, duck
- The feathers of birds are used for decorations
- Birds are also used for the pollination of seeds and fruit dispersal
- Some birds like Ostriches are attractive to tourists
- Some species of birds are used for biological control
Importance of Mammals
- Most mammals serve as source of food for human beings example cows, sheeps
- Mammals help in production of manure example manure from cows, goats
- The bones of mammals are used for production of animal charcoal
- Most wild animals in national parks and game reserves attract tourists
- Some domestic mammals such as cows and donkeys are trained to perform human duties such as cultivation of crops


Everyone loves what you guys are usually up too. This kind of clever work and coverage!
Keep up the good works guys I’ve included you guys to
blogroll.
You will be earning loyalty points anytime you location a bet at Casino Las Vegas.
Wow! After all I got a web site from where I can in fact obtain helpful data regarding my study and knowledge.
My blog post: Quick Shred Keto Pills Ingredients
Wow, that’s what I was searching for, what a data!
present here at this webpage, thanks admin of this web site.
Check out my web-site – Luminas Pain Patch Reviews
It’s very easy to find out any matter on net as compared to textbooks, as I found this article at this web site.
I am in fact grateful to the holder of this website who has
shared this enormous article at at this place.
Here is my site … Quick Shred Keto Reviews
Thanks for a marvelous posting! I really enjoyed reading it, you can be a
great author.I will remember to bookmark your blog and
will come back at some point. I want to encourage that you
continue your great job, have a nice day!
Great beat ! I wish to apprentice even as
you amend your site, how can i subscribe for a weblog site?
The account helped me a applicable deal. I have been a little
bit familiar of this your broadcast provided
brilliant transparent concept
I like examining and I believe this website got some truly utilitarian stuff on it!
Here is my web blog Jolly CBD Gummies| Jolly CBD| Jolly CBD Gummies Review| Jolly CBD Gummies Reviews| Jolly CBD Gummies Cost}
Hello everyone, it’s my first visit at this website, and piece of writing is truly
fruitful designed for me, keep up posting these posts.
I actually still can not quite assume that I could always be one of those studying the important tips
found on your site. My family and I are really thankful for your generosity and for giving me the chance to
pursue my chosen career path. Appreciate your sharing the important information I acquired from your web page.
Feel free to surf to my webpage … Luminas Pain Relief Patch
I visited multiple blogs except the audio quality
for audio songs present at this web page is in fact superb.
That is a very good tip especially to those new to the blogosphere.
Short but very accurate info? Many thanks for sharing this one.
A must read post!
Check out my blog post :: Jocosa CBD Gummies
Hello colleagues, its great paragraph concerning tutoringand entirely
defined, keep it up all the time.
Here is my page :: Jolly CBD Reviews
We’ve compiled a list of the most common ones, and provided
detailed answers to them in our FAQ.
I am impressed with this site, real I am a big fan.
Review my homepage … Jolly CBD Gummies Reviews
I happen to be commenting to let you be aware of what
a really good experience my friend’s girl developed studying your web site.
She realized a wide variety of details, most notably what it is like to have a marvelous helping
heart to let others without difficulty learn selected extremely tough subject
matter. You truly did more than her desires.
Thanks for giving these essential, trustworthy, edifying and also unique guidance
on the topic to Kate.
Here is my web blog – Jolly CBD Gummies| Jolly CBD| Jolly CBD Gummies Review| Jolly CBD Gummies Reviews| Jolly CBD Gummies Cost}
My family every time say that I am wasting my time here at net, but I know I am getting familiarity everyday by reading such pleasant articles.
Hi there Dear, are you actually visiting this web page on a regular basis, if so
then you will without doubt get fastidious knowledge.
my homepage: Testoryze Male Enhancement Reviews
David Dierking, who writes TheStreet’s ETF Concentrate joined TheStreet to talk about
sports betting ETF’s and the sector as a whole.
Due to the nature of the occasion you are betting on, you should adapt a strategy accordingly.
Check Their License –All new betting websites require to be licensed.
Any event in any multisport competitors in which
an individual is participating.
I got what you mean,saved to favorites, very nice website.
my blog Full Body Bio Labs
Hey very interesting blog!