TOPIC 2: SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT | BIOLOGY FORM 1
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Saves life
- Reduces fear of death
- Brings hope and encouragement to the patient
- Relieves the victim’s pain
- Prevents the illness or injury from becoming worse
- Helps a person to recover from shock
- It shows spirit of helping each other.
Aid kit is a small box which is used to keep instruments and chemicals
for First Aid. The first Aid kit should be placed in a safe and
accessible place.
A pair of scissors
Gauze
Assorted bandages
Adhesive plasters
Cotton wool
New razor blade
Gentian violet (GV)
Petroleum jelly or Vaseline
Safety pins
Iodine tincture or spirit
Soap
Anti-pain (pain killers) e.g. Panadol
Sterilized forceps and pins
Liniment
A pair of tongs
Antibiotic solution
A pair of scissors:is used for cutting dressing materials such as gauze, bandages·
Gauze:is used to cover the wound to prevent dirt and micro-organisms from entering.
Assorted bandages: are used for securing an injured part in order to protect and support it.
Adhesive plaster:are used for covering minor wounds/cuts and grazes·
Cotton wool:is used for cleaning and drying wounds and applying medicine·
New razor blade:used for cutting any flaps of skin when cleaning the wound.
Gentian Violet (GV):is used as an antiseptic to clean wounds.
Petroleum jelly or Vaseline:used for treatment of burns
Safety pins:used for holding/securing bandages.
Iodine tincture or spirit:used for cleaning wounds to reduce bleeding.
Soap:is used for washing wounds, hands and medical facilities.
Anti-pain (pain killers):used to reduce pain.
Sterilized forceps and pins:are used for removing splinters and grit from wounds.
Liniment:used to reduce muscle pains.
A pair of tongs:used for holding pieces of bandages when cleaning the wounds.
Antibiotic solution:is used for applying in the wounds for killing micro-organisms.
- She/he should have ability to assess the problem and give immediate and appropriate help.
- She/he must be able to act quickly, quietly, calmly
- She/he should be sympathetic to the victim
- She/he
should be able to recognize dangerous signs and give immediate help for
example detecting immediately if -breathing has stopped or is failing
-there is severe bleeding-poisoning-fractures - She/he should be able to help the injured person without unnecessary movement
First Aider should keep himself/herself safe to avoid dangers from the
patient. Some of the dangers that s/he may face include infection by
pathogens such as viruses and bacteria.So they should:
Wear protective gloves to avoid contact with blood
Wear eye protection
Wear masks and gowns.
Drowning
Muscle cramps
Bleeding
Poisoning
Hiccups
Suffocation
Bruises Fainting Burns Sprain Bone fracture Snake bite
poisonous snake has two fangs one on each side of the upper jaw. The
fangs are as sharp as needles. At the root of the fang there is a poison
gland. When the snake strikes, it jabs downwards hitting the skin with
its fangs and releases a few drops of venom.
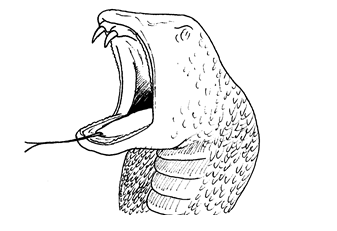
- Immediate pain and swelling after the bite
- The skin becomes purple One or two punctured points may be seen where the fangs passed through the skin
are armed with a single curved stinger in the tail. Through this, they
inject powerful venom that may produce convulsions and temporary
paralysis.
- Apply tourniquet
- Put ice on the injured area to relieve pain and prevent spread of the poison
- Treat for shock
- <!–[endif]–>Rush the person to the hospital
someone is bitten by a dog, keep the dog under observation to see
whether it has rabies. Rabies is one of the worst diseases known. It is
caused by a virus which is present in the saliva of the infected animal.
the animal has rabies, it will become restless, excitable, refuse to
eat and barking tone will change. Later the dog then starts barking
excessively.
<!–[endif]–>Wash your hands well with soap and water
Wash the wound thoroughly with soap and water to remove the animal’s saliva using running water.
Cover the wound with clean gauze.
Bandage it carefully
Take the victim to the hospital.
- Spider bites :
Some spiders have a harmless venom to man. But the black spiders can be
dangerous to man. The injured person becomes weak and dizzy, feels
nauseated and the muscles of the stomach may become hard especially in
children. - Black and fire ants, bees : When a
person has been stung by e.g. bees, severe pains are felt
immediately.The person may be shocked, itching and swelling may follow.
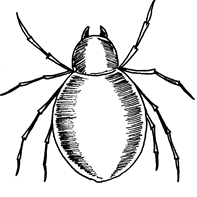
Remove the insect’s sting
Apply household ammonia and ice cubes
Treat for shock
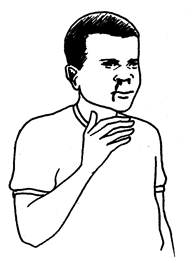
you are with a person that is chocking, first notice if person can
talk, breath or cough. If so stay with that person until the air way is
cleared by coughing.

First stand behind the chocking victim
Put your arms around the person, placing your firsts just below the breast bone as shown above.
Give a series of quick, sharp upward and inward thrusts
every household there are different kinds of things which are
poisonous. Some are deadly even on a very small dose. Others may be more
or less harmless when taken in small quantities.
Look for the poison
Identify the poison
Neutralize the poison by giving the victim plenty of milk to drink or egg white or water.
Induce vomiting if the poison is not strong acid or alkali as these are corrosive substance.
If the problem is severe, rush him or her to the hospital.
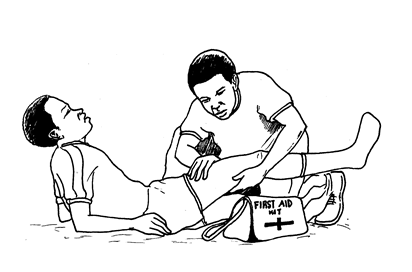
Severe pain around the injured part
Lack of movement
Swelling
Fainting or shock
Treat for a shock
Keep the patient absolutely quite
Prevent further damage to injured part by using a splint.
Bring the bone back into fixed position
Bandage it firmly in place so that it does not slip out again
- Bad news
- Severe illness
- Heavy bleeding
- Dehydration
- Severe burns
- Accident
Lie down the person with his feet higher than his head
Loosen the belt and shoes
If the person is conscious give him some tea or any soft drink.
Treat his/her wounds if any
Stop any bleeding Keep the person warm if he/she feels cold
Switch off the electricity immediately
If
not possible to switch off the electricity, take the victim away from
the source of electricity using a dry wooden material or rope.
Loosen any tight clothes
If the person is unconscious, apply mouth to mouth respiration
Treat for shock
Take the person to the hospital immediately
Wash your hands using water and soap
Wash the bruised part
Apply cold clothes or ice immediately to reduce pain and swelling
If swelling continues take the victim to the hospital
- Allergic reactions
- Diseases e.g. malaria
- Physiological condition e.g. pregnancy
- Food poisoning
- Unpleasant smell or taste
- Drinking a lot of water when thirsty.
Give the person a rehydration drink or oral rehydration salts solution.
Allow the person to have a complete rest
If vomiting continues, take the patient to the hospital.

Lay the victim down
Massage the cramped area gently
Apply some anti-cramp ointment to the affected area
If the problem persists seek for a medical help
Severe pain
Loss of movement
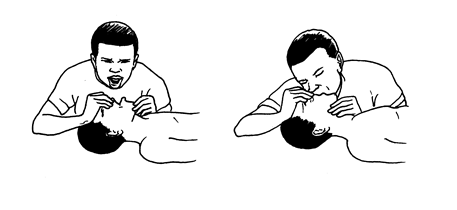
Lay the person on his back and tilt his head backwards so that his mouth falls forward
Pull the tongue forward.Use a dry cloth to hold the tongue.
Hold his nose close with your fingers
Carry
out mouth to mouth breathing by blowing gently into the person’s mouth
about 30 times a minute but do not blow too hard.This process is called artificial respiration.
Keep the person warm.
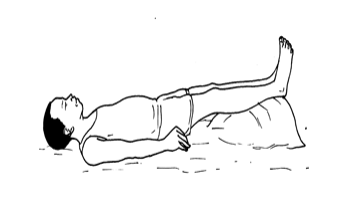
is caused by a temporary fall in the blood supply to the brain,
sometimes brought on by emotional shock or prolonged standing.
Keep the victim lying down with his/her legs raised in order to maintain blood pressure in the brain.
Do not try to warm the victim.
Loosen any tight clothing around the neck, chest and waist.
Supply the patient with plenty of fresh air by fanning or mouth to mouth respiration.
If there is no improvement rush the victim to the hospital.
Severe
bleeding with blood flowing out rapidly must be stopped at once by
pressing with fingers directly on the wound or pressing the edges of the
wound together.
Lay the victim down.
If the wound is in a limb raise it provided it is not fractured.
When the bleeding has slowed down press a pad of material over the wound and tie it rapidly in place.
If blood oozes through, apply more material on top of the original pad.
Wash your hands well by using soap and water
Wash the wound
Cover the wound with clean dressing dipped in iodine solution and bandage the wound
High blood pressure
Rheumatic fever Or
Injury
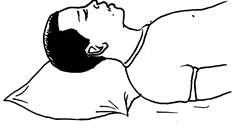
Let the victim sit quiet. This makes the heart beat to slow down and hence reduces bleeding.
Let the victim lean the head slightly backward or make him/ her lie down on his/ her back.
Press on the side of the nose where the blood is flowing for about 10 minutes.
Allow the victim to breath through the mouth
Apply cold, wet compression over the nose and face. If this does not work take the victim to the hospital
burn is caused by dry heat e.g. flame of hot object. A scald is caused
by a steam or boiling water. The treatment is the same for both burns
and scalds except that in scalds any wet clothing should be carefully
removed while in burns clothing should be left in place. If clothes are
burning cover the victim with a heavy blanket to cut off the air supply.
the burning limb into clean cold water or press the affected area
gently with an ice block. Do not break the blisters. Cover the injured
area with clean dry cloth to keep away bacteria entering the damaged
tissue. If the situation is serious take the victim to the hospital
immediately.
Strip off all clothing which has been contaminated by the chemical.
Wash the affected area with plenty of water.
Apply moist packs soaked in a weak solution of baking soda.
Vinegar can be used for alkaline burns.
Pulling out the tongue
The victim may swallow finely crushed ice
Holding a breath for a long time may also help
Children can be given a teaspoonful of a weak solution of sodium bicarbonate or lemon juice.
- Double-cross
- First Aid
- Re-cross
- First Aid kit
- First Aid kit
- First Aider
- A calmer
- A planner
- Venom
- Nails
- Fangs
- Tail
- Choking
- Shivering
- Fainting
- Vomiting
- Kept moving
- Sent to hospital
- Given a heavy blow
- Given a fluid
- Choking
- Drowning
- Fainting
- Hiccups
- Identify the poison
- Induce vomiting
- Give plenty of milk
- Eating plenty of pepper
- Bone dislocation
- Hiccups
- Shock
- Fainting
- First Aid kit is an immediate help which is given to a sick or injured person before sending him/her to the hospital _________
- One of the importance of First Aid is to give hope the victim _________
- A good First Aider should have the ability to recognize dangerous signs ___________________
- Venom is the poison of the snake __________________
- Liniment is used to reduce muscle pains _____________
- It is not necessary to offer First Aid to a snake bite person _______________
- Giving First Aid prolongs the problem ______________
- First Aid
- First Aid kit
- Venom
- Fainting
- Choking
- State any four importance of the First Aid
- List down five components of the First Aid kit
- State any four qualities of the First Aider
- Cotton wool
- Iodine tincture
- Soap
- Assorted bandages
- Petroleum jelly
- Snake bite
- Drowning
- Fainting
- Bruises
- Poisoning
- What is shock?
- State any four causes of shock
- Enumerate the ways of preventing shock.
accident is something unexpected that may cause injury and sometimes
lead to death. Accidents may be difficult to predict and prevent.
Bites e.g. snake bite, insect bite, scorpion bite and dog bite.
Burns
caused by hot liquids, cooking pot, lamps, hot food, steam, burning
wood, charcoals and those caused by corrosive chemicals such as
concentrated acids and strong alkalis.
Falls, e.g. wall falls, tree falls, bed falling, etc.
Cuts and scratches caused by knives, hoes, razor blades and other sharp objects.
Choking caused by drinks, food or objects
Electric shock due to unguarded electric outlets and lightning.
Poisoning caused by taking chemicals and excessive intake of medicines.
Foreign bodies in the eye, ear and nose
Drowning which may occur in very small amount of water such as baths, ponds, pit latrines, wells and water tanks.
Nose bleeding, bruises, suffocation, fainting etc.


- Mention common accidents that can happen at home and school
- State the ways of preventing accidents
- How can you maintain peace and safety at home and school?
Medicines and potential poisonous chemicals should be kept out of reach of children.
Children should be monitored closely when playing.
Sharp objects like broken bottles, razor blades and laboratory equipments should be well disposed of.
Laboratory chemicals should be labelled and if possible appropriate warning signs should be indicated.
One should not take medicine unless prescribed by the doctor.
Bushes and tall grasses around the house should be cut to avoid harbouring snakes, bees and other dangerous animals.
Students should observe and adhere to laboratory rules.
Walls and trees that are at a risk of falling should be dismantled or cut down respectively.
Flammable substances should be properly kept.
Pits
dug around the house should be buried. Pools should be drained if
possible and all water storage containers should be properly covered.
Avoid
using charcoal to warm oneself during night when sleeping as continued
inhalation of carbon monoxide from the charcoal may lead to death
Burning candles should be put off when sleeping.
Players should adhere to game rules.
Laboratory doors should open outwards for easy exit in case of fire. Emergence door is also necessary for this case.
Equipment like hoes, axes and knives should be properly kept
Turn off all the gas taps after experiment.
Avoid risk behaviours such as playing near deep ponds, playing with knives, alcoholism etc.
Dangerous things such as drugs should be kept away from children’s reach
Report any dangerous event that someone engages in.
Be positive and supportive to each other.
Social problems occurring at home or school should be solved keenly.
One should be good to him/herself.
Parents should give their children education on how to live and interact with others.
can be defined as unwanted materials or substances that are left after
you have used something. Waste materials or substances are unwanted
because the good part of them has been removed or it is not used.
- Solid wastes
- Sludge wastes
- Liquid wastes
- Gaseous wastes
are wastes which comprise of about 73% of the solid wastes. Example of
solid wastes include house hold solid wastes such as vegetable, fruit
and garden wastes, papers, cans, plastics, bread wrappers, broken
glassware, batteries from watches, radios, mobile phones, etc. and
junked automobiles.
are semi-solid wastes i.e. wastes which are neither solids nor liquids,
for example, a mixture of livestock urine and cow dung.
are wastes which are in the form of liquid or watery materials. They
contain less than 25% solid substances. Example of liquid wastes include
water from sinks, wash basins and baths, urine, industrial effluent,
oil spills and agricultural chemicals e.g. insecticides and pesticides.
are waste materials which are released into the atmosphere in gaseous
state. Examples of gaseous wastes are carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide,
sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide.
of the gaseous wastes come from industries and automobile exhaust
fumes, laboratories and burning of organic materials such as plastics
and polythene bags.
- Hazardous waste
- Non- hazardous wastes
These are harmful wastes which can endanger the health of living
organisms. Examples of hazardous wastes include paints, engine oil, car
batteries, used syringes, soiled dressings, organochlorides, radioactive
elements and heavy metals e.g. lead and mercury.
These are wastes which are not harmful in that they do not endanger the
health of living organisms. Examples of such wastes include packing
materials, papers, plastics, cans, water from wash basins, baths, etc,
vegetable, fruit and garden wastes and glass.
- Recycled wastes
- Non- recycled wastes
are wastes which can be used to manufacture new products. The used
materials are recycled instead of being thrown away. Examples of waste
materials which can be recycled include metals, glass, papers, cow dung,
beer bottles and plastic bags.

- By their physical states
- As hazardous and non- hazardous wastes
- As recycled and non-recycled wastes.
disposal is the process of getting rid of waste materials that people
generate or the act of getting rid of unwanted materials and items of no
value or in excess.
- Recyclable wastes should be separated from non- recyclable wastes
- Greater precaution should be observed when disposing hazardous wastes and it is important to separate them from other garbage
- It is important to use protective materials e.g. gloves when collecting and disposing wastes.
- Food and yard wastes should be separated from other garbage so as to be delivered to a compost site
- It is necessary to treat sewage before it is empted into the water bodies
- Sewage systems should be checked from time to time to control leakages
- Radioactive wastes should be disposed off by putting them in tanks and dipping them in deep oceans.
cities and towns have waste collecting departments or private firms
that gather municipal solid wastes from homes and other buildings.
involves hauling garbage to an area owned by a community or a private
firm. Land disposal may range from unsanitary open dumps to sanitary
landfills.
May produce bad odors
Ruin the area’s appearance
Rain water drains through refuse and carry harmful substances to nearby streams and to water used for drinking.
Decomposing wastes produce flammable gas called methane and methane explosions may result.

are intended to protect the environment. The waste is packed firmly by
tractors and covered with specially manufactured materials. The
covering is done in order to limit blowing papers, odors, fires and run
off of polluted water.
A secure sanitary land fill is lined with materials that prevent water
from carrying leachates (dissolved substances) from the refuse into
underground water supplies.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
is intended to collect smaller quantities of wastes. The waste bins are
placed along the corridors or in every room or house which in turn is
emptied into big waste bins.
is water that contains waste matter produced by human beings. It is
also called waste water. Sewage comes from toilets and sinks of homes,
restaurants, office buildings and factories Sewage system involves the
use of collection pipes or pit latrines where the sewage is periodically
removed and transported to a sewage works where it is treated to make
it harmless.
is the process of reusing the materials instead of throwing them away.
The waste products are used to manufacture the same or different
products such as:
Cardboard or cow dung can be used to generate Biogas.
Thermoplastics can be melted and remoulded.
Organic wastes produced domestically or commercially can be composted.
Kitchen refuse can be used to feed animals such as dogs, pigs, cattle, etc.
Newspapers, magazines cartons and packing materials can be used to manufacture tissue papers.
In Tanzania coffee husks are converted into a form of charcoal which is used for cooking
Coconut and agricultural wastes can be converted into papers.
Jute wastes can be converted into hard boards.
Sewage and factory wastes can be purified to an extent that can be pumped into storage tanks and used for all domestic purposes.
Glass bottles can be used for storing specimens or medicines.
reduction is deliberate effort to produce fewer wastes. For example,
people can reduce waste by buying items that can last longer or have
less packing.
Produce bad odors
Ruin the areas appearance
Decomposing
wastes produce flammable gas called methane and this may result to
explosion of the gas which may cause a loss of material property and
human life.
Rain water drains through refuse and carry harmful
substances to nearby streams and water used for drinking which may later
lead to eruption of diseases like cholera and may kill organisms found
in water
Poor disposal of clinical wastes on land fill site may encourage bacterial breeding leading to possible infections in the area
Unregulated dumps where waste is burned in the open can cause smoke and foul smelling air.
Burning
may also result into production of air pollutants which may affect the
ozone layer and possible cause of respiratory diseases.
- Mention the four types of wastes according to their physical states.
- State the different ways through which wastes can be disposed
- Name two examples for each of the following
- Solid wastes
- Liquid wastes
- Gaseous wastes
- Hazardous wastes
- Non-hazardous wastes
- Recyclable wastes
- Non-recyclable wastes
- Waste
- Waste disposal
- Plastics
- Oil spills
- Broken glassware
- Junked automobiles
- Sludge wastes
- Urine
- Liquid wastes
- Gaseous wastes
- Waste
- Sewage
- Waste disposal
- Incineration
- Liquid wastes
- Solid wastes
- Gaseous wastes
- Sludge
- Open dump
- Incineration
- Waste reduction
- Landfill
- Carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxide and sulphur dioxide are examples of gaseous wastes ______________
- One way of disposing wastes is by recycling ___________
- In the classrooms, wastes such as papers, pens and plastic materials should be thrown anywhere through the windows _________
- One of the problems of poor waste disposal is that it reduces spread of diseases _________________
- More than 80% of the liquid wastes contain water _________
is a state of physical, mental and social wellbeing. It involves more
than just the absence of disease. A truly health person not only feels
good physically but also has a realistic outlook on life and gets along
well with other people.
Nutrition:Balanced diet provides all the food substances needed by the body for health growth and development.
Exercise:Exercises
help to keep the body healthy and fit. Vigorous exercises strengthen
muscles and improve the function of the circulatory and respiratory
system.Physical fitness benefits both physical and mental health and
helps the body to withstand stress.
Rest and sleep:Help
to overcome fatigue and restore energy to the body. Everyone needs rest
and sleepRest and relaxation are as important as sleep. After strenuous
work or exercise a person may need a period of total rest.
Cleanliness:Cleanliness
prevents the growth of bacteria and other germs that can cause
diseases. A regular bath or shower keeps the body free from dirt and
odour. It also helps to prevent skin infections.
Medical and dental care:Regular
check ups by dentist and physician play an important role in
safeguarding health. Doctors recommend that people seek medical care at
first sign of illness. Early care can result in quicker cure and lower
medical costs.
Avoiding risk behaviours:Careful
observation over a range of life style factors indicate that positive
changes can bring about corresponding change in health status Risk
behaviours that need to be avoided include: Smoking: cigarette smoking
increases respiratory diseases such as bronchitis and increases risk of
death from lung cancer and heart attack; Alcoholism: heavy, long term
drinking has several effects on the body. It affects nervous system,
cause liver disease (cirrhosis), etc; Drug abuse: drugs can cause
addiction, long term harmful effects, disruption of normal life and some
can lead to death.
during childhood strongly influence a person’s mental health throughout
life. Children remain dependent for many years. At this period they
learn certain guidelines for relating to other people. Thus children
develop the knowledge necessary to deal with difficult situations in
life. This knowledge helps them maintain good mental health throughout
life.
development does not end when a person reaches adulthood. An
individual’s mental health continues to change from time to time. These
changes result from daily circumstances that cause either pleasure or
pain to the person.
handling is essential for avoiding both mental and physical illness.
Feelings of stress are the body’s response to any threatening or
unfamiliar situation. Causes of stresses include the following:
Most severe stress may result from divorce or loss of job.
Stress
can also occur even in pleasant situations such as: Watching a football
game, Waiting for a lovely one to return from a trip, etc.
Physical or emotional illness
High blood pressure
Stomach ulcers
Regular exercises and sufficient sleep strengthens the body resistance to stress
Relax by resting
Taking a walk
Meditating
Working with hobby
personal relationships with friends and relatives provide opportunities
for communication, sharing and emotional growth.Such relationships also
provide strength and support for dealing with challenging situations or
personal problems.
- Enables people to enjoy life and have opportunity to achieve their goals.
- Sets someone free from attack by diseases.
- Enables people to work effectively and efficiently.
- Good health helps people to participate in social issues.
- Enables mothers to deliver healthy babies.
- Raises the family economy which in turn ensures peace and security within the family and the surrounding community.
is the ability of the body to resist certain diseases and
poisons.Immunity can also be defined as the ability of the body to
defend itself against infectious agents, foreign cells and even abnormal
cells such as cancer cells
immune system comprises of a group of cells, molecules and tissues that
help defend against disease and other harmful invaders.
invaders include disease-causing organisms (pathogens) such as
bacteria, fungi, protozoa, virus and worms.A key feature of immune
system is its ability to destroy foreign organisms, leaving the body’s
own health tissues alone.
- Natural immunity
- Artificial immunity
- Natural active immunity
- Natural passive immunity
Natural active immunity:This
immunity develops in a body after a natural infection. After infection,
antibodies are produced in the body. The antibodies normally reside in
the blood or in other parts of the body. The body can make more
antibodies whenever the pathogen tries to attack the body again.
Natural passive immunity:This
type of immunity is achieved during development of the foetus where
antibodies pass from the mother to the foetus through placenta or
through the mother’s milk after the baby is born. The antibodies
disappear from the infant a few months after birth.
- Artificial active immunity
- Artificial passive immunity
is the process of introducing a vaccine into the body of an animal in
order to increase its ability to produce antibodies. These antibodies
protect the person if he/she is exposed to the actual disease.
Most vaccines contain disease-causing bacteria or viruses that have been killed.
Others consist of the live germs but in a weakened form or attenuated.
Toxoid vaccines are made from poisons produced by disease-causing organisms.
These poisons are chemically treated so that they provide immunity without causing disease.
Some vaccines are made from parts of disease-causing organisms.
have been developed against many diseases such as chicken pox,
diphtheria, influenza, measles, meningitis, mumps, pneumonia,
poliomyelitis, cholera, rabies, rubella (German measles), tetanus,
whooping cough and yellow fever.Vaccines can be taken through,
injection, rubbing or the mouth (orally).
type of immunity involves the injection of serum into the body of an
organism. Serum contains antibodies that have been formed in another
person or animal. It provides immediate protection from infection and
lasts for weeks or months and after that period there are no antibodies
left in the body and therefore no immunity.
- Alcohol and other toxic drugs.
- Lack of immunisation.
- Lack of proper balanced diet.
- Inability of the body to produce antibodies and white blood cells.
- Pathogens of HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
Eating balanced diet regularly to maintain good health
The body should be washed daily and hair combed regularly
Teeth should be brushed after every meal
The nails should be cut short
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
Wear clean and ironed clothes
Avoid risk behaviours like smoking cigarettes, drinking alcohol, prostitution and others
Wash your hands with soap before and after meals and after visiting a lavatory
Have enough sleep and rest.
Take regular exercises to maintain fitness
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
Underwears should be changed regularly
Bedding should be changed regularly
Respect
– an individual should have good respect such as: showing great respect
to elders by helping and greeting them decently; being polite and
humble; and talking in a clear and calm voice.
Tidiness
– every body should look smart all the time. An individual should: keep
the bedroom neat; brush shoes; wear clean and ironed clothes; cut nails
and hairs short; comb or plait the hair nicely, etc.
Discipline
– an individual should be well disciplined e.g. avoid using bad
language; cover, your mouth when sneezing, yawning or coughing; and
portray good postures e.g.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
sitting properly in class and at home.
Good eating habits
(table manners) which include the following: Eating at regular time
intervals; Avoid talking with food is in the mouth; Do not pile food up
on your plate. Serve yourself with a reasonable amount while considering
others; In case the food given is not good, make an excuse that you are
not hungry or not feeling well rather than showing or saying that the
food is not good; Don’t tell stories that will make others laugh when
eating; Always wash your hands before and after eating
Putting things in proper order:
All objects in the surrounding should be kept properly and in a right
place e.g.: Rubbish should be disposed as required; Books should be kept
in shelves; Cooking and eating utensils should be kept well in the
cupboards; Clothes should be properly ironed, folded and kept.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
of personal hygiene and good manners include towel, soap, comb, brush,
basin, toothbrush, a pair of scissors, razor blades, water and
cosmetics.
is the adolescent period. It is the period when one experiences
physiological changes in the body. The physiological changes mark the
beginning of adolescence.Puberty begins the age of 10 to 12 years for
girls and 11 to 14 years for boys.
- Both sexes should wash their bodies regularly
- During menstruation, girls should use good quality sanitary towels or pads and change them as necessary.
- Boys should undergo circumcision and females should avoid female genital mutilation
- Underwears should be washed and changed regularly
- Both
boys and girls should avoid irresponsible sexual behaviours such as
prostitution and rape so as to keep away from sexually transmitted
diseases (STDs) - Hair in the armpits or pubic areas should be shaved or trimmed.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Reduces chances of pathogen infection
- Enhances social acceptance in the society
- Prevents one from getting choked while eating
- Maintains natural body state
- Maintains personality of an individual in the society
- One becomes respected by others
- Maintains health of the body and mind
Infection is the invasion of disease-causing micro-organisms into the body.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
Disease is
the disturbance of the normal state of the body. It is a disordered
state of an organ or organism. Infections normally lead to diseases.
- Infectious (communicable) diseases
- Non-infectious (non-communicable) diseases
are diseases which can be transmitted from one person to another
person. Communicable diseases are normally caused by micro- organisms
like viruses, bacteria, fungi and protozoa, etc
of infectious diseases include: malaria, typhoid, tuberculosis,
cholera, gonorrhoea, syphilis, ebola, AIDS, chlamydia, etc.
Droplet of liquid
Air
Food or water
Sexual intercourse
Touch or contact e.g. ringworm
An intermediate organism called a vector e.g. malaria by mosquito and bubonic plague by rat flea.
- Epidemic disease
– a disease that affects a larger number of people in a short period of
time in a region for example, cholera, meningitis, bubonic plague, rift
valley fever (RVF), tuberculosis, etc.SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Pandemic disease – a communicable disease which is wide spread over a country continent or the whole world, for example HIV/AIDS, etc.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Endemic disease
– a communicable disease which occurs in an area continuously for
example, bilharzia, sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), malaria (an
endemic disease in tropical regions) and cholera (endemic in Asia).
- Lung cancer
- Asbestosis
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Asthma
- Coronary (heart) diseases
- Alcoholism
- Kwashiorkor: lack of protein
- Marasmus: lack of both carbohydrate and proteins
- Night blindness: lack of Vitamin A
- Beriberi: lack of Vitamin B1
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Scurvy: lack of Vitamin C
- Rickets: lack of Vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorous
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Anaemia: lack of iron
- Goitre: lack of iodine
- Excessive bleeding (haemophilia): lack of Vitamin K
- Colour blindness
- Haemophilia
- Sickle cell anaemia
- Albinism
- Down’s syndrome
- Klinefelter’s syndrome
- Turner’s syndrome
- Long sightedness due to weakening of eye muscles
- Arteriosclerosis (hardening of arteries)
- Arthritis – ageing of joint and bone tissues
- Schizophrenia
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Senile dementia
- Depression
- Diabetes mellitus
- Diabetes inspidus
- Cretinism
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
CHOLERA
MALARIA
TYPHOID
TUBERCULOSIS (T.B)
MENINGITIS
AMOEBIC DYSENTRY (AMOBIASIS)
PLAGUE
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
TRYPANOSOMIASIS (SLEEPING SICKNESS)
BILHARZIA (SCHISTOSOMIASIS)
ATHLETE’S FOOT
GONORRHOEA
SYPHILIS
CLAMYDIA
GENITAL HERPES
GENITAL WARTS
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
HEPATITIS B
TRICHOMONIASIS
CANDIDIASIS
Explain the causes, symptoms, mode of transmission and effects of common infections and diseases
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Severe watery diarrhoea and vomiting
- Body weakness
- Fast and weak pulse
- Low blood pressure
- Wrinkled skin and sunken eyes due to dehydration
- Rapid loss of weight
- Food or water borne material contaminated with faeces from infected person
- Handling of contaminated objects
- Vectors e.g. flies moving from human faeces to food.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
High fever. Fever may be continuous, irregular or twice daily.
Vomiting
Lack of appetite
General body weakness
Joint pains
is transmitted by a female anopheles mosquito.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
The mosquito sucks blood
containing plasmodium from the infected person and introduces them into
the body of a health person. In rare cases malaria can be transmitted
through blood transfusion from the infected person to a health person.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
Mild fever
Slight abdominal pains
Diarrhoea
Vomiting
Ulceration and rupture of intestine
Contaminated water and food
Handling of contaminated objects
Vectors of the disease e.g. houseflies
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
Loss of weight
Coughing
Fever
Chest pain
Blood in the sputum
Through droplet infection
Through drinking milk from infected cattle
T.B is common in overcrowded areas with poor sanitation
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Wash hands after visiting toilet or latrine
- Food should be well cooked and drinking water should be boiled and well filtered
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
Hands should be washed before and after eating
Food should be well covered
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
Utensils should be washed thoroughly
Maintain general environmental cleanliness
The infected person should be isolated
Special precautions should be taken when handling the infected person
Vaccination is possible
The disease can be treated by using antibiotics such as tetracycline, chloramphenicol
Administering rehydration salt solutions
May lead to death
Extra medical expenses
Failure to perform daily activities
Spraying insecticides to destroy adult mosquitoes
Introducing fish eating mosquito into stagnant water e.g. Gambusia that feed on mosquito larvae.
Draining stagnant water to remove the breeding sites for mosquitoes
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
Use of mosquito nets to prevent mosquitoes from biting people
Screening the windows with mosquito-proof wire-mesh to prevent entry of mosquitoes in the house through the windows.
Wear long-sleeved shirts and trousers to prevent mosquito bites.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
Mosquito larvae and pupa can be killed by spraying oil into stagnant water that cannot be drained.
Taking regular weekly doses of preventive drugs to kill parasites on entry.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
Cutting bushes around the houses to destroy shelter for mosquitoes
Using mosquito repellents to flee away the mosquitoes
Can cause death
Can lead to mental confusion in case of cerebral malaria
Paralysis and unconsciousness
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
Drowsiness
Anaemia
Miscarriage
Inability to participate in economic activities
Increased medical expenses
Wash hands after visiting the toilet
Food and water must be protected from dust and flies
Wash hands before and after eating
Drink boiled water and eat properly cooked food; fruits should be washed thoroughly before being eaten.
Vaccination can also help to control the disease
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Can cause death
- May cause ulcers and finally rupture of the intestine
- Enlarged spleen
- Elimination of the conditions under which TB thrives e.g. overcrowding, poverty level living and inadequate nutrition.
- Observing general personal hygiene, especially when coughing and sneezing.
- Early
BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin) VaccineThe Vaccine may be used for
either of two reasons:(i) Protecting newly-born babies or children at
particular risk of infection.(ii) Immunization of young persons or at
risk groups in the community. - Keeping children, in particular, away from risk situations.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- The use of sterilized milk and pasteurized dairy products
- Contact tracing so that risk to others may be minimized
- Causes a number of deaths.
- Abscess full of pus may form near the lump in the spine.
- Shortening and thickening of the chest in case of TB of the spine.
stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus, and AIDS for Acquired Immune
Deficiency Syndrome. It is thought that AIDS originated from central
Africa. The HIV Virus which causes the disease appears to have migrated
Via Haiti to the USA.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
The term acquired means become infected and immune
deficiency means lack of immunity
transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted
diseases (STDs) and venereal diseases (VDs), are infections that are
commonly spread by sex, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex and
oral sex. Most STIs initially do not cause symptoms.
are more than 30 different sexually transmissible bacteria, viruses and
parasites.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
The most common STIs they cause are gonorrhoea, chlamydia,
syphilis, trichomoniasis, chancroid, genital herpes, genital warts,
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and hepatitis B infection.
caused by HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus).The Virus attack the
body’s immune system weakening it and making it more susceptible to
infections and some cancers.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
is important to realize that, infection with the HIV virus does not
necessarily result in AIDS. As with other diseases, some people remain
symptomless and are said to be carriers.
are two major types of HIV Viruses, HIV 1 and HIV 2.HIV 1 is the most
predominant virus and it is more easily transmitted while HIV 2 occurs
in a small number of people in West Africa, Angola, Mozambique and some
parts of India.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
It is less virulent.
in the body can you find HIV viruses? The virus in the body can be
found in the following body fluids: blood, semen, vaginal fluid, tears,
saliva and urine and breast milk.It is observed that semen, blood and
vaginal fluids are more infectious.
person infected with HIV may start to show signs of illness as from few
weeks to many years. The infected individual may experience the
following signs and symptoms:
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Tremendous loss of weight
- Persistent fever
- Chest pain
- Diarrhoea for no obvious cause
- Coughing for more than one month
- Shortness of breath getting worse over several weeks
- Itchy skin rashes
- Thrush in the mouth and throat
- Loss of hair
- Sexual intercourse with an infected person
- Transmission from the mother to the baby during pregnancy, birth or breast feeding.
- Sharing sharp objects with infected people e.g. sharing needles, razor blades, tooth brushes etc.
infected person may exhibit a variety of conditions. Common bacterial,
fungal and viral infections attack the victim. These are known as
opportunistic infections. They include diseases like pneumonia, T.B,
meningitis, candidiasis, cancer e.g. Kaposi’s sarcoma, etc.
- Use the ABC method to prevent the disease: A-Abstain from sex B– Be faithful to your only partner C- use Condom.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
This means that you are advised to abstain completely from sexual intercourse. If you can’t then have one faithful partner and if this seems to be difficult then use condoms.
- Avoid sharing sharp tools with the infected individuals
- Blood transfusion should be done prior to HIV screening
- Pregnant mothers should attend clinic so that they get treatment that will prevent HIV transmission from the mother to the baby.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Avoid
all the risk behaviours, situations and practices that may enhance HIV
transmission. The risk behaviours include drug abuse, prostitution,
rape, anal sex, oral sex, alcoholism, unsafe sex, roaming in bars, guest
house, etc.
- Practising safe sex
- Applying non- penetrative sex e.g. kissing, hugging, etc.
- Delaying technique e.g. I’m required at home just now lets meet tomorrow
- Discouraging/negative words e.g. I’m HIV positive
- Discouraging peer pressure
- Engaging in sports and games which distract one’s mind from concentrating to sex.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Showing
a sense of dislike to express the way you are by wearing T-shirts, caps
with various messages e.g. ‘say no to sex’, ‘practice safe sex’, ‘Mimi nimepima wewe je?’, ‘AIDS kills’ etc
- Avoid sexual intercourse. It is possible to live a healthy normal life without having sexual intercourse.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Use
a condom correctly every time you have vaginal sex. It is often hard to
be sure that your partner is truly faithful and unaffected. - Avoid multiple partners. Don’t have more that one sexual partner.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Avoid alcohol and drug abuse as they affect your decision making ability thus leading you to unsafe sex.
- Avoid
sharing needles and other skin piercing tools. Needles can be
contaminated and HIV can survive in a syringe for a month or longer.SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Avoid
contracting other STIs because they increase the chances of HIV and
AIDS infection. For those who have been infected, they must get proper
treatment from a qualified medical practitioner. - Avoid risky
behaviours such as going to night clubs, negative peer pressure and
taking alcohol or drug abuse. These might put you in danger of being
infected.SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Prevent mother to child transmission by: (a)
counselling and treating the mother; (b) using caesarean section as a
mode of delivery; (c) use of alternative feeding (milk) instead of
breastfeeding; and (d) not sharing breast milk. - Prevent transmission through organ and tissue transplants by screening both the donor and the patient.
- Prevent
minor injuries which might lead to infection.SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
This can be achieved
through:(a) use of gloves; (b) use of sterile instruments; (c) avoiding
direct contact with contaminated body fluids;(d) proper handling of
contaminated human waste; and (e) decontaminating soiled surfaces and
lined.SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Effective treatment of the infected through: (a)
administering anti-retroviral therapy; and (b) prompt treatment of
opportunistic infections.
- It enables them to prolong their lives in case they are administered with ARVs.
- It reduces fear of death.
- It enables them to perform their daily activities without fear.
- It reduces depression and self dislike.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
who are infected with HIV need care and support form their friends,
families and the community, especially when they are ill.
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
Friends and
family members sometimes worry that they might be infected when caring
for a person with HIV.
cannot be passed on by touching, hugging, coughing, or sharing eating
utensils. It is possible for people who are infected with HIV to live
long healthy lives. You can help those who are infected by:
showing love, respect and support;
knowing the facts about HIV/AIDS and talking openly about the disease;
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
helping to reduce stress and stressful situations;
helping to provide balanced and nutritious meals;
seeking for support from family and friends as well as from other people who are HIV positive;
encouraging them to live with hope;
encouraging them to be active. Do not stop them from doing things they like;
spend
time with the sick person. For example help them to prepare their
meals, clean their rooms, make their beds and take them to a walk if
they can walk. Encourage family and friend to do this too;
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
encouraging
them to get treatment if they are sick. Most infections are easily
treated and cured, even if a person is HIV positive.
Cleaning their houses, utensils, clothes, etc.;
trying to relieve any pain the person may be feeling, for example by administering pain killers; and
treating them with respect and dignity making them as comfortable as possible.
- There
may be situations where you need to clean up body fluids or blood from
someone infected with HIV.SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
Do not touch body fluids such as blood, stool
and urine with your bare hands. It is important to use rubber or
plastic gloves or other barriers such as plastic bags or thick cloth to
prevent direct contact. Make sure that you have these easily available
at all times.SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Wash the gloves or plastic bags in hot water every
time after you have used them. Keep clothes and bedding with blood,
diarrhoea or body fluids away from other washings. - Wash the bedding and clothes with soap. Hang them where there is a plenty of sunshine and air circulation to dry well.
- Do not share toothbrushes, razors, skin piecing instruments, or needles
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
- Cover your wounds with a clean and sterile bandage. Buy disposable gloves so that once used they are discarded.
- Dispose off properly the vomits or bandages used when dressing wounds.
- Learn
about the ways HIV can and cannot be transmitted. Talk to your friends
and family. Contact your local clinic for more informationSAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
stigma and discrimination exist worldwide, although they manifest
themselves differently across countries, communities, religious groups
and individuals. Possible consequences of HIV-related stigma could be:
SAFETY IN OUR ENVIRONMENT
loss of income and livelihood
loss of marriage and childbearing options
poor care within the health sector
withdrawal of caregiving in the home
loss of hope and feelings of worthlessness
loss of reputation







